y = ((x - 1)^2)/(2*x)
Q01. Diagram
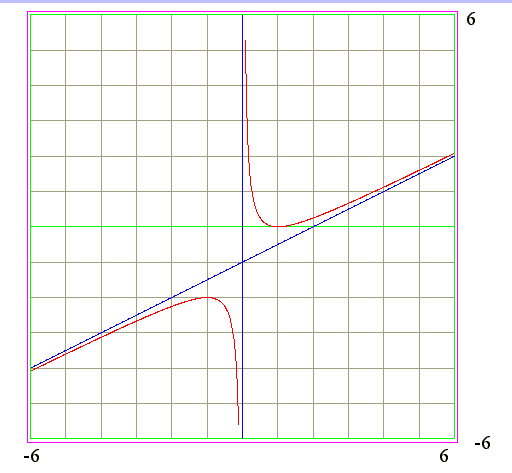
|
Go to Begin
Q02. Describe the curve by values of x and y
Properties of the curve
- Sign of x and y
- x < 0 and y < 0. In 3rd quadrant
- x > 0 and y > 0. In 1st quadrant
- x = 1 and y = 0
- Asymptote
- x = 0 and y = infinite. Hence x = 0 is vertical asymptote
- x = infinite, y = x/2 - 1. Hence asymptote is a line y = x/2 - 1
- Curve : x = -infinite to x = 0
- x < 0 and y < 0 : Curve is in 3rd quadrant
- x = -infinte and y = -infinite
- x = 0 and y = -infinite
- Curve of y is from -infinite to (x1,y1) then to -infinite
- Curve is between line y = x/2 - 1 and x = 0
- Hence curve increase from -infinite to a maximum point (x1,y1)
- From maximum point (x1,y1) decreases to -infinite when x = 0
- Hence Curve is concave downward
- Curve : x = 0 to x = +infinite
- x > 0 and y > 0 : Curve is in 1st quadrant
- x = 0 and y = +infinite
- x = 1 and y = 0
- x > 1 and y from 0 to +infinite
- Curve of y is from infinite to 0 when x = 1
- Then from (1,0) to (infinite, infinite)
- Curve is between line y = x/2 - 1 and x = 0
- Hence curve decrease from +infinite to a minimum point (1,0)
- From minimum point (1,0) increases to infinite when x = infinite
- Hence Curve is concave upward
- From curve we see
- Maximum at (-1,-2)
- Minimum at (+1, 0)
Go to Begin
Q03. Find signs of y' and y" from curve
Signs of y'
- y' > 0 if x < -1. Hence curve is increasing
- y' = 0 if x = -1. Hence curve has maximum point
- y' < 0 if x between -1 and 0. Hence curve is dcreasing
- y' < 0 if x between 0 and 1. Curve is decreasing
- y' = 0 if x = 1. Hence curve has minimum point
- y' > 0 if x > 1. Hence curve is increasing
- y" < 0 if x < 0. Hence curve is concave downward
- y" = 0 if x = 0. Hence curve has turning point
- y" > 0 is x > 0. Hence curve is conave upward
Go to Begin
Q03. Find y'
Formula to find derivative of y = f(x)/g(x)
- dy/dx = (g(x)*f'(x) - g'(x)*f(x))/(g(x)^2)
- y' = (2*(x - 1)*(2*x) - 2*(x - 1)^2)/(4*x^2)
- = (x - 1)*(4x - 2*(x-1))/(4*x^2)
- = (x - 1)*(2*x + 2)/(4*x^2)
- = (x - 1)*(x + 1)/(2*x^2)
- If x < -1, y' > 0. Curve is increasing
- If x = -1, y' = 0. Curve has maximum point
- If x > -1 and x < 0, y' < 0. Curve is decreasing
- If x > 0 and x < 1, y' < 0. Curve is decreasing
- If x = 1, y' = 0. Curve has minimum point
- If x > 1, y' > 0. Curve is increasing
Go to Begin
Q04. Find y"
Second derivative y"
- y" = (2*x*(2*x^2) - 4*x*(x^2 - 1))/(4*x^4)
- = (4*x^3 - 4*x^3 + 4)/(4*x^3)
- = 1/(x^3)
- x < 0, y" < 0. Curve is concave downward
- x = 0, y" not exist. Curve in change from concave down to up
- x > 0, y" > 0. Curve is concave upward
Go to Begin
Q05. Discussion
Graphic solution
- The graphic solution is clear determine the signs of y, y' and y"
- The maximum and minimum points can only be estimated
- Without graph, the concavity can only be determined
- by the asymptotes
- By change of increasing from decreasing
- Graphic solution will not need the knowledge of calculus
Go to Begin