-
Q01 |
- Diagram : Locus of parabola
- Q02 | - Locus : Equation of parabola
- Q03 | - Sketch parabola using ruler
- Q04 | - Parabola : Polar form
- Q05 | - Parabola : Special function
- Q06 | - Reference
- Q02 | - Locus : Equation of parabola
Q01. Diagram : Locus of parabola
|
Go to Begin
Q02. Locus : Equation of parabola
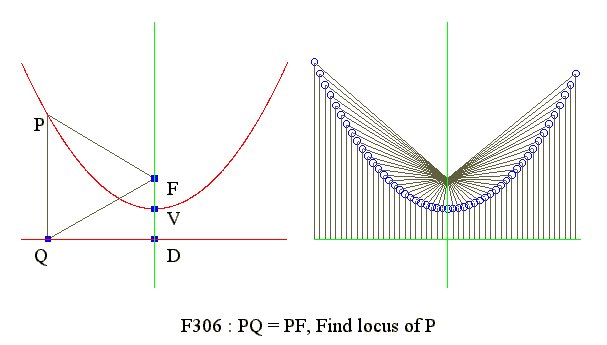
Locus of parabola
- Point P to fixed point F and fixed line DQ has same distance
- Find locus of point P
- Where F is focus and DQ is the directrix
- Coordinates : P(x, y), F(0, 0) and Q(x, y + D)
- PF = Sqr(x^2 + y^2)
- PQ = y + D where D is distance from focus F to directrix
- By definition PF = PQ
- Sqr(x^2 + y^2) = y + D
- Square both sides
- x^2 + y^2 = (y + D)^2
- x^2 = 2*y*D + D^2
- Hence the equation of parabola is y = (x^2)/(2*D) - D/2
- a = 1/(2*D)
- b = 0
- c = -D/2
- The parabola : y = (x^2)/(2*D) - D/2
- Focus F at (0, 0)
- Vertex V at (0, -D/2)
- Directrix equation is y = -D
- Vertex
- xv = -b/(2*a) = -(-6)/(2*1) = -3
- yv = F(xv) = (-3)^2 - 6*(-3) + 8 = -1
- Distance from focus to directrix is D = 1/(2*a) = 0.5
- Coordinates of focus
- xf = xv = -3
- yf = yv + D/2 = -1 + 0.5/2 = -0.75
- Equation of directrix : y = yv - D/2 = -1 - 0.5/2 = -1.25
- Equation of principal axis : x = xv = -3
Go to Begin
Q03. Sketch parabola using ruler
Method
- Parabola Sketch using ruler
Go to Begin
Q04. Parabola : Polar form
Polar form
- 1. R = D/(1 - cos(A))
- 2. R = D/(1 + cos(A))
- 3. R = D/(1 - sin(A))
- 4. R = D/(1 + sin(A))
- Parabola in polar forms
- Definition
- In ellipse : R/(D + x) = e and e is less than 1
- In parabola : R/(D + x) = 1
- In Hyperbola : R/(D + x) = e and e is greater than 1
- Proof
- Ellipse Prove R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A))
Go to Begin
Q05. Parabola : Special forms
R = sec(A/2)^2 is parabola
- sec(A/2)^2 = 1/(cos(A/2)^2)
- cos(A/2)^2 = 1 + cos(A)
- Hence R = sec(A/2)^2 = 1/(1 + cos(A))
- It is parabola
- It open to the left when A = 180
- D = 1
- It is same as x = a*y^2 + b*y + c when a is negtive
- csc(A/2)^2 = 1/(sin(A/2)^2)
- sin(A/2)^2 = 1 - cos(A)
- Hence R = csc(A/2)^2 = 1/(1 - cos(A))
- It is parabola
- It open to the right when A = 0
- D = 1
- It is same as x = a*y^2 + b*y + c when a is positive
Go to Begin
Q06. References
Exercises : y = x^2
- 1. Find the directrix
- 2. Find coordinate of focus
- 3. Find equation of directrix
-
Subject |
Parabola
Go to Begin
