-
Q01 |
- Diagram : Locus of hyperbola
- Q02 | - Equation of locus
- Q03 | - Study ((x - 1)/4)^2 - ((y - 2)/3)^2 = 1
- Q04 | - Hyperbola : Polar fotm
- Q05 | - Find locus of 9*x^2 - 25*y^2 + 18*x + 50*y - 191 = 0
- Q06 | - Reference
- Q02 | - Equation of locus
Q01. Diagram : Locus of hyperbola
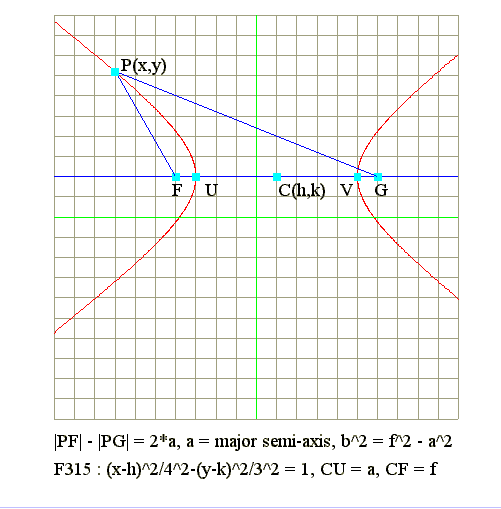
|
Go to Begin
Q02. Locus of hyperbola : (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1
Question
- Two fixed point F and G. A moving point P(x, y)
- Find the locus if Abs(PF - PG) = 2*a
- Let two fixed point be F(-f, 0) and G(f, 0)
- Hence PF = Sqr((x + f)^2 + y^2)
- Hence PG = Sqr((x - f)^2 + y^2)
- By definition : Abs(PF - PG) = 2*a
- PF^2 = PG^2 + 4*a^2
- Sqr((x + f)^2 + y^2) - Sqr((x - f)^2 + y^2 = 2*a
- Sqr((x + f)^2 + y^2) = 2*a + Sqr((x - f)^2 + y^2
- Square both sides
- (x + f)^2 + y^2 = 4*a^2 + 4*a*Sqr((x - f)^2 + y^2) + (x - f)^2 + y^2
- Simplify we have
- 4*x*f = 4*a^2 + 4*a*Sqr(x - f)^2 + y^2)
- Sqr((x - f)^2 + y^2) = x*f/a - a
- Remove square root
- (x - f)^2 + y^2 = (x*f/a - a)^2
- x^2 - 2*x*f + f^2 + y^2 = (x^2)*(f^2)/(a^2) - 2*x*f + a^2
- (1 - (f^2)/(a^2))*(x^2) + y^2 = a^2 - f^2
- (a^2 - f^2)*(x^2) + (a^2)*(y^2) = a^2 - f^2
- Let b^2 = f^2 - a^2
- Hence -(b^2)*(x^2) + (a^2)*(y^2) = -(a^2)*(b^2)
- Divide both sides by -(a*b)^2
- We have (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1
- This is the hyperbola with principal axis y = 0
- a and b are semi-axese
- Focal length f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2)
Go to Begin
Q03. Study the curve of ((x - 1)/4)^2 - ((y - 2)/3)^2 = 1
Question :
- 1. Find focal length f
- 2. Find principal axis
- 3. Find asymptotes
- 4. Find Coordinates of vertex and foci
- 5. Find domain and range
- 1. Find f
- Since a = 4 and b = 3
- Hence f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 5
- 2. Principal axis is y = 2
- 3. Asymptotes
- 3*(x - 1) = 4*(y - 2)
- 3*(x - 1) = -4*(y - 2)
- 4. Vertex and foci
- Let center be (h, k). Hence h = 1 and k = 2
- xu = h - a = 1 - 4 = -3 and yu = k = 2
- xv = h + a = 1 + 4 = +5 and yv = k = 2
- xf = h - f = 1 - 5 = -4 and yf = k = 2
- xg = h + f = 1 + 5 = +6 and yg = k = 2
- 5. (y - 2)/3 = Sqr((x - 1)/4)^2 - 1)
- y = 3*Sqr((x - 1)^2 - 16)/4 + 2
- Domain : (x - 1)^2 - 16 >= 0
- Hence (x - 1) > + 4 or x > 5
- Hence (x - 1) < - 4 or x < -3
- Range :
- y is from 0 to +infinite for +Sqr
- y is from 0 to -infinite for -Sqr
- No y values between x = -3 and x = 5
Go to Begin
Q04. Hyperbola : Polar form
Definition
- Let D = distance from focus to directrix
- R = Point P(x, y) to Focus F(0, 0)
- Point P to directrix = D + x
- If R/(D + x) = e and e is greater than 1, it is hyperbola
- Proof
- R/(D + x) = e
- R = (D + x)*e
- Since in polar coordiantes x = R*cos(A)
- Hence R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A))
- e = f/a
- e = 1 is parabola
- e < 1 is ellipse
- e > 1 is hyperbola
- 1. R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A))
- 2. R = (D*e)/(1 + e*cos(A))
- 3. R = (D*e)/(1 - e*sin(A))
- 4. R = (D*e)/(1 + e*sin(A))
-
Hyperbola
in polar form
Go to Begin
Q05. Find locus of 9*x^2 - 25*y^2 + 18*x + 50*y - 191 = 0
Change it to standard hyperbola form
- Use completing the square
- 9*(x^2 + 2*x + 1 - 1) - 25*(y^2 - 2*y + 1 - 1) - 191 = 0
- 9*(x + 1)^2 - 25*(y - 1)^2 = 225
- ((x + 1)/5)^2 - ((y - 1)/3)^2 = 1
- Hence this is a hyperbola
- Center (-1, 1)
- Focal length f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 5
- e = f/a = 5/4 = 1.25
- D*e = (b^2)/a = 9/5 = 1.8
- Polar form R = 1.8/(1 - 1.25*cos(A))
Go to Begin
Q06. Reference
Reference
Go to Begin
