-
Q01 |
- Diagram : Hyperbola x*y = 1
- Q02 | - Compare x*y = 1 with (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1
- Q03 | - Rotate x*y = 1 45 degrees
- Q04 | - Eliminate x*y term
- Q05 | - Using eliminate method for x*y = 1
- Q06 | - Equation of directrix of Hyperbola x*y = 1
- Q07 | - Find focal length of (x + 1)*(y - 2) = 1
- Q02 | - Compare x*y = 1 with (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1
Q01. Diagram : Hyperbola x*y = 1
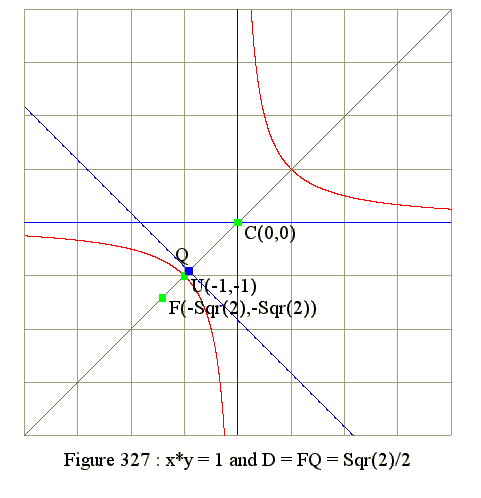
|
Go to Begin
Q02. Compare x*y = 1 with (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1
Diagram of x*y = 1
- Vertex U at xu = -1 and yu = -1 or U(-1, -1)
- Vertex V at xv = +1 and yv = +1 or V(+1, +1)
- Center C(0, 0)
- Principal axis is y = x
- CU = Sqr(xu^2 + yu^2) = Sqr(2)
- Corresponding hyperbola if rotate 45 degrees
- (x/Sqr(2))^2 - (y/Sqr(2))^2 = 1
- Hence semi-axese : a = Sqr(2) and b = Sqr(2)
- Hence CF = f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 2
- Hence Focus F at (-Sqr(2), -Sqr(2))
- D*e = (b^2)/a = Sqr(2) and e = f/a = Sqr(2)
- Hence D = 1
- Principal axis y = 0
- a = Sqr(2) and b = Sqr(2)
- Center at (0, 0)
- Vertex U at (-Sqr(2), 0)
- Focal length f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 2
- Focus F at (-2, 0)
- D*e = (b^2)/a = Sqr(2)
- e = f/a = Sqr(2)
- Hence D = 1 = distance from focus F to directrix
- x*y = 1 and (x/Sqr(2))^2 - (y/Sqr(2))^2 = 1 are congruent
- The difference is the principal axese
- For (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1, principal axis is y = 0
- For x*y = 1, principal axis is y = x
Go to Begin
Q03. Rotate x*y = 1 with angle 45 degrees
Question : Rotate x*y = 1 45 degrees
- 1. Find semi-axese
- 2. Find focal length
- 3. Find corrdinates of foci
- Rotation matrix
- | +cos(A) +sin(A) |
- | -sin(A) +cos(A) |
- (u, v) to (x, y)
- u = +x*cos(A) + y*sin(A)
- v = -x*sin(A) + y*cos(A)
- Rotation matrix
- | +cos(A) -sin(A) |
- | +sin(A) +cos(A) |
- (x, y) to (u, v)
- x = +u*cos(A) + v*sin(A)
- y = -u*sin(A) + v*cos(A)
- x = +u*cos(A) - v*sin(A)
- y = +u*sin(A) + v*cos(A)
- Hence x*y = 1
- (+u*cos(A) - v*sin(A))*(+u*sin(A) + v*cos(A)) = 1
- Since cos(45) = Sqr(2)/2 and sin(45) = Sqr(2)/2
- Hence (Sqr(2)*u/2 - Sqr(2)*v/2)*(Sqr(2)*u/2 + Sqr(2)*v/2) = 1
- Since (x - y)*(x + y) = x^2 - y^2
- Hence (1/2)*(u^2 - v^2) = 1
- Hence (u/Sqr(2))^2 - (v/Sqr(2))^2 = 1
- Hence a = b = Sqr(2)
- Hence f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 2
- Vertices of (u/Sqr(2))^2 - (v/Sqr(2))^2 = 1
- (-Sqr(2), -Sqr(2)) and (Sqr(2), Sqr(2)) in UOV coordinates
- Vertices of x*y = 1
- (-1, 1) and (1, 1) in XOY coordinates
- Foci of (u/Sqr(2))^2 - (v/Sqr(2))^2 = 1
- Since f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 2
- Hence coordinates of foci are (-2, -2) and (2, 2) in UOV coordinates
- Foci of x*y = 1 in XOY coordinates
- From diagram CF = 2
- Hence xf = 2*cos(1.25*pi) = -Sqr(2) and yf = 2*sin(1.25*pi) = -Sqr(2)
- Hence coordinates of focus (-Sqr(2), -Sqr(2)) and (Sqr(2), Sqr(2))
Go to Begin
Q04. Eliminate x*y term
Question
- Equation : F(x,y) = A*x^2 + B*x*y + C*y^2 + D*x + E*y + F = 0
- Rotation : Transform x and y to u and v by roration angle t
- (1) x = u*cos(t) - v*sin(t)
- (2) y = u*sin(t) + v*cos(t)
- Let B'=0.
- (C - A)*sin(2*t) + B*cos(2*t)=0
- Hence tan(2*t)=B/(A - C)
- Angle t = arctan(B/(A - C))/2
- Chnage A'*u^2 + C'*v^2 + D'*u + E'*v + F' = 0 to
- Using completing square : ((u - h)/a)^2 + ((v - k)/b)^2 = 1
- Since no u*v we can use completing square nethod
- Hence we find h and k
- We can also find a and b
- We can also find vertice and focal length f
Go to Begin
Q05. Using eliminate method for x*y = 1
Change x*y = 1 to (x/a)^2 - (y/b)^2 = 1
- A = 0, B = 1, C = 0, D = 0, E = 0 and F = -1
- Find A', B', ....
- Rotate angle t = arctan(1/(0 - 0)/2 = 45 degree
- A'
- = A*cos(t)^2 + B*cos(t)*sin(t) - C*sin(t)^2
- = 0 + 1*cos(45)*sin(45) - 0
- = 1/2
- B'
- = (C - A)*sin(2*t) + B*cos(2*t)
- = 0
- C'
- = A*sin(t)^2 - B*cos(t)*sin(t) + C*cos(t)^2
- = 0 - 1*cos(45)*sin(45) - 0
- = -1/2
- D' = +D*cos(45) + E*sin(45) = 0
- E' = -D*sin(45) + E*cos(45) = 0
- F' = F = -1
- Hence equation becomes : (1/2)*u^2 - (1/2)*v^2 - 1 = 0
- Hence (u/Sqr(2))^2 - (v/Sqr(2))^2 = 1
- That is a = Sqr(2) and b = Sqr(2)
- That is f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2)) = 2
Go to Begin
Q06. Equation of directrix of Hyperbola x*y = 1
Question
- Find equation of directrix
- Equation directrix is y = -x + c
- From Diagram we see that
- CF = CQ + QF
- QF = D = 1 is the distance from F to directrix
- CQ = CF - QF = 2 - 1
- Find c using right triangle CQP
- Let P be intersection of directrix with y-axis
- Since angle CQP = 90 and angle CPQ = 45 degrees
- Hence QP = CQ = 1.2929
- Hence CP = Sqr(PQ^2 + CQ^2)
- = Sqr(2*(1.2929)^2)
- = Sqr(3.34318)
- = 1.828436
- Hence c = -1.828436
- Hence y = - x - 1.828436
- 2nd method to find c : Using coordinate of Q (-0.9142, -0.9142)
- Since CQ = 1.2929
- Hence xq^2 + yq^2 = CQ^2
- Since xq = yq
- Hence xq = -0.9142 and yq = -0.9142
- Substitute xq, yq into y = -x + c
- Hence c = -18284
Go to Begin
Q07. Find focal length of (x + 1)*(y - 2) = 1
Use translation
- Translate origin of x*y = 1 to (-1, 2)
- We have (x + 1)*(y - 2) = 1
- Hence (x + 1)*(y - 2) = 1 is congruent to x*y = 1
- It is congruent with (x/Sqr(2))^2 - (y/Sqr(2))^2 = 1
- Hence focal length f = Sqr(a^2 + b^2) = 2
Go to Begin
