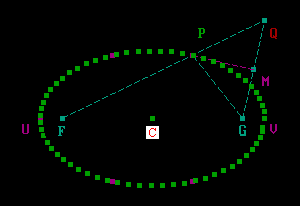
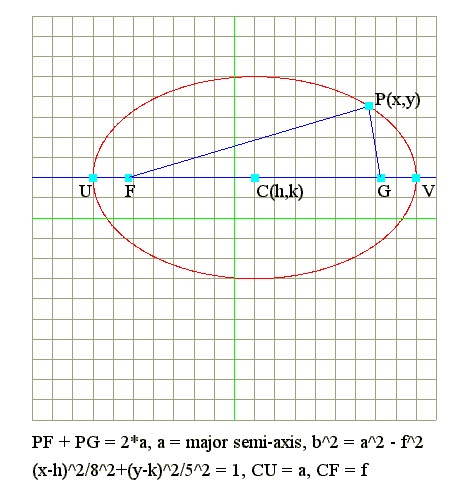
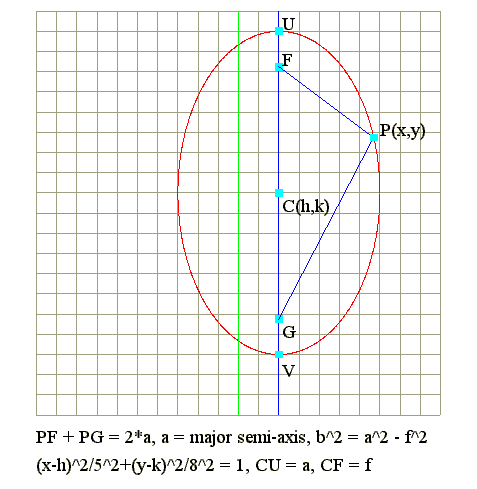
Q1. Defintion : PF + PG = 2*a is ellipse
- If PF + PG = 2*a, then the locus of P is ellipse.
- Equation of locus : (x-h)^2/a^2 + (y-k)^2/b^2 = 1.
- Center is at C(h,k).
- CF = CG = f = focal length = Sqr(a^2 - b^2).
- CU = CV = a = major semi-axis.
- FU = CU - CF = a - f.
- Principal axis is y = k if a greater than b.
Q2. Definition : R/PQ = e is an ellipse in polar coordiante
- Equation of locus is R = D*e/(1-e*cos(A)).
- Where focus F is (0,0) and angle A is PF making with x-axis.
- Directrix is y = -D where D is the distance from F to direcrtix.
- PQ is distance from P to directirx and Q is on directrix.
- R = PF and PQ = D + x where x = R*cos(A).
- e = f/a and e is less than 1 for ellipse.
Q3. How to find D ?
- Since e = f/a.
- When A 180 and cos(A) = -1.
- Hence R = UF = D*e/(1+e) = f - a.
- Hence D = (f-a)*(1+e)/e
Example : x^2/5^2 + y^2/3^2 = 1. Find equation of directrix.
- Principal axis is y = 0.
- a=5 and b=3. Hence f = Sqr(a^2-b^2) = 4
- e = f/a = 4/5 = 0.8.
- Use polar form : R = D*e/(1-e*cos(A)) and F is the origin.
- When A = 180 and con(A) = -1 and R = UF = a - f.
- Hence a - f = D*e/(1+e).
- Hence D = (a-f)*(1+e)/e = (5-4)*(1+0.8)/0.8 = 2.25.
- Hence equation of directrix is x = -f - D = -6.25.
- Use polar form : R = D*e/(1+e*cos(A)) and F is the origin.
- When A = 0 and con(A) = 1 and R = VG = a - f.
- Hence a - f = D*e/(1+e).
- Hence D = (a-f)*(1+e)/e = (5-4)*(1+0.8)/0.8 = 2.25.
- Hence equation of directrix is x = f + D = 6.25.
|