
Skeletal System
Muscular System
Circulatory System
Skin
Teeth
Injuries
Training
more to come...


Support for organs and tissues
Allows movement
Store of minerals

Very dense, making it able to provide protection, support and strength.
Spongy Bone Tissue
Inner and end of bones contain large spaces shaped like a honey comb and these are filled with red marrow. Spongy bone tissue makes up most bone tissue of short flat and irregular shaped bones.
Hollow and tubular with a long shaft. Can withstand heavy stress and pressure and are very important in bearing weight.
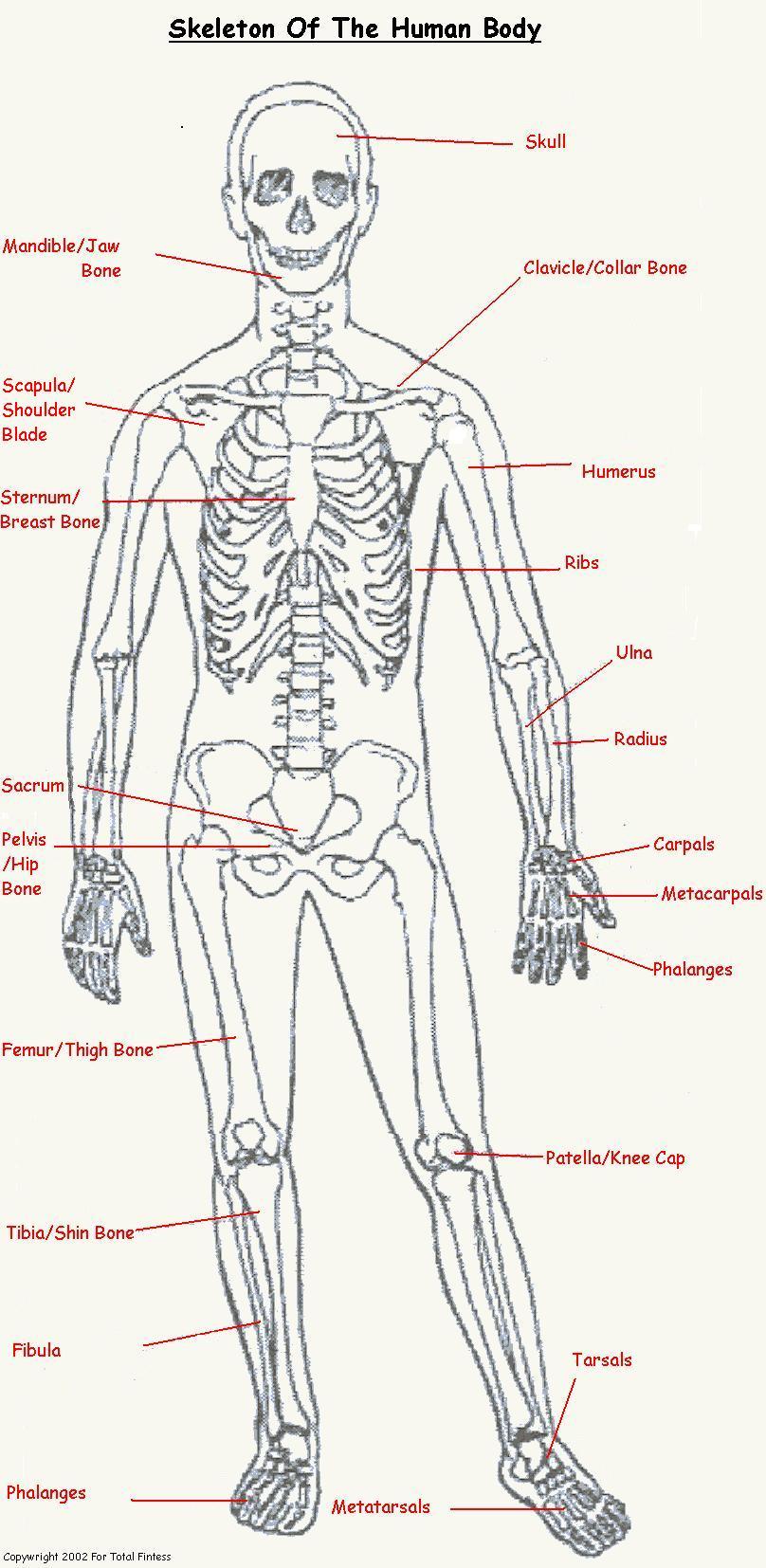
Examples of these types of bones are humerus, femur, radius, tibia, phalanges see skeleton.
Short Bones
Shaped like a cube and almost equal in length and width. Spongy texture except for compact bone at the ends.
Examples of these types of bones are the carpal and tarsal bones see skeleton.
Flat Bones
generally thin with a layer of spongy bone in the centre. Broad shape and a smooth surface allowing for a large area of muscle attachment.
Example of these types of bones is the scapula see skeleton.
Irregular Bones
Irregular shaped bones can't be grouped into either of the three above categories so they are all the other bones in the bosy that do not fall nder the above catergories.
Examples of these types of bones are the vertebrae and some facial bones see skeleton.
Sesamoid bones are classified because of where they are found rather than the shape of them. Sesamoid bones are found in tendons where pressure develops.
Examples of these types of bones are the patella see skeleton.