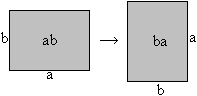
Commutative law for multiplication. ============================================================
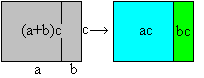
Distributive law
for multiplication.
============================================================
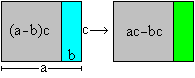
Product of
a difference and a number.
============================================================
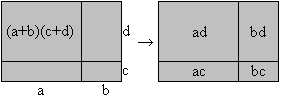
Product of
two sums.
============================================================
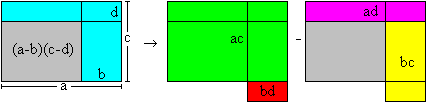
Product of
two differences.
============================================================
You can see both cubes and the six rectangular parallelepipeds in 3D-view:
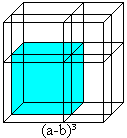
Cube of a difference
The formula is (a-b)�=a�-3a�b+3ab�-b�. You convert it to (a-b)�=a�-3ab(a-b)-b� for an illustration. ...... You take the drawing of the formula (a+b)�=a�+3a�b+3ab�+b� from above and replace a by the difference a-b.
Then the edges are (a-b)+b with different combinations (on the left).
The term (a-b)� is illustrated by the blue cube (on the right).
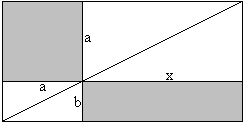
a2=bx
============================================================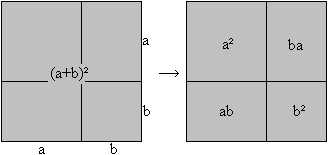
[a+b]
2=a2+2ab+b2
============================================================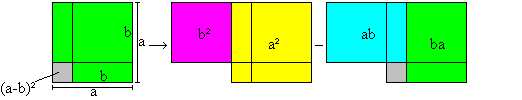
[a-b]
2=a2-2ab+b2
============================================================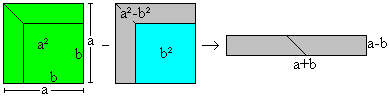
[a2-b2]=[a-b][a+b]
============================================================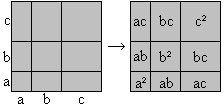
[a+b+c]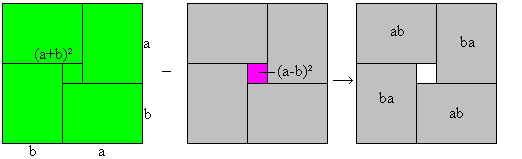
[a+b]2-[a-b]2=4ab
============================================================
Pythogoras' theorem
============================================================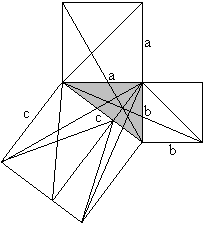
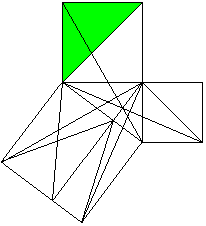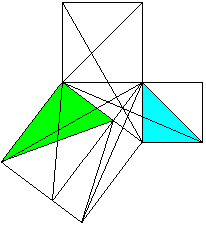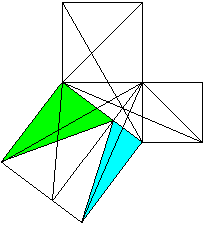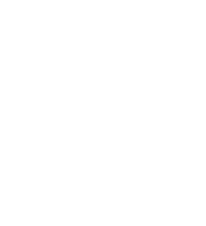
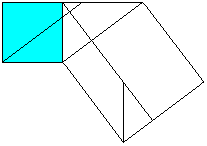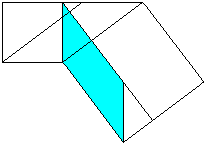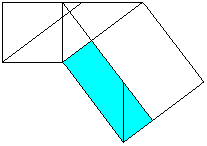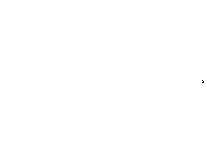
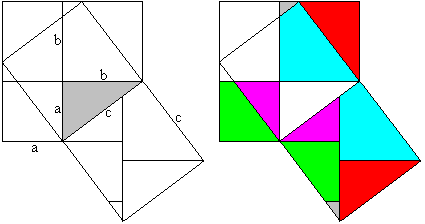
Classical proof of Pythogoras theorem using triangles.
============================================================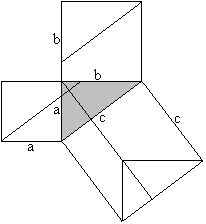
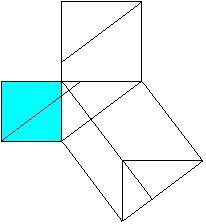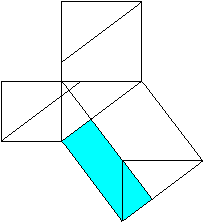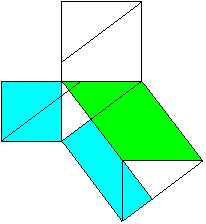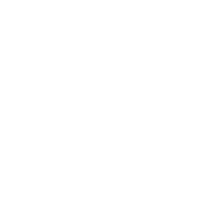
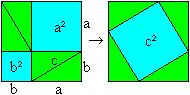
a2+b2=c2
============================================================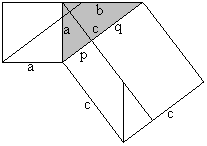
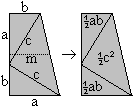
a2=cp (Similarly you can show that b2=cq
============================================================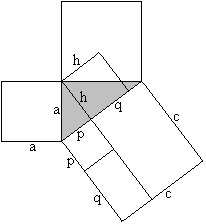
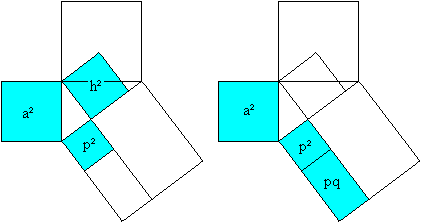
a�=p�+h� (Pythagorean theorem), a�=pc=p�+pq (Euklid's theorem),
hence h�=pq
============================================================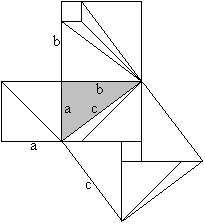
a�+b�=c�
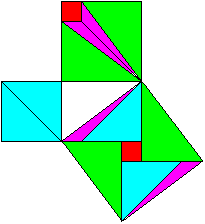
============================================================
a�+b�=c�
============================================================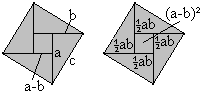
c�=(a-b)�+2ab; c�=a�+b�
============================================================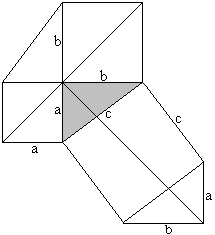
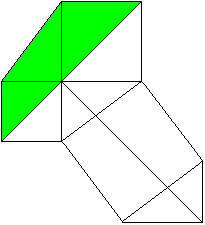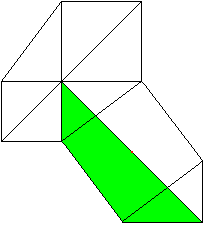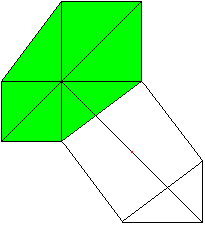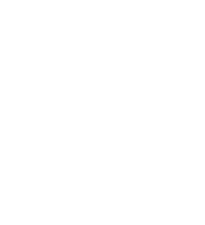
a�+b�=c�
============================================================
a�+b�=c�
============================================================
You use the formula of the area of a trapezium [A=mh, here h=a+b and m=(a+b)/2]
(a+b)�/2=c�/2+2*(1/2*ab) or a�+b�=c�
============================================================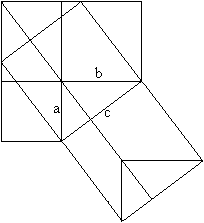
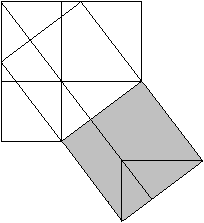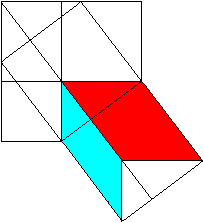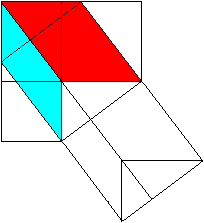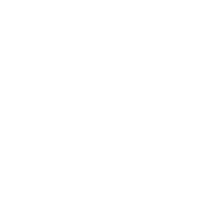
c�=a�+b�
============================================================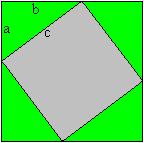
(a+b)�=c�+4*(1/2ab); a�+b�=c�
============================================================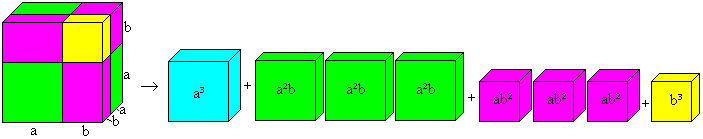
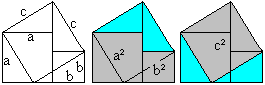
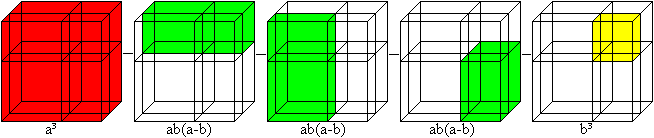
(a+b)�=a�+3a�b+3ab�+b�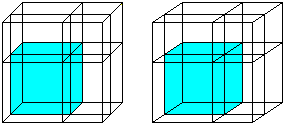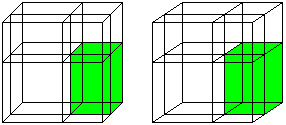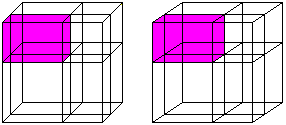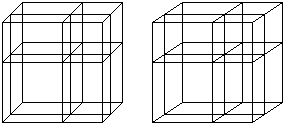 ============================================================
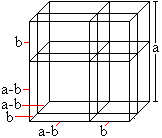
============================================================
......
You recieve the blue cube, too, if you take away the three green bodies and the yellow cube from the red cube: (a-b)� = a�-3ab(a-b)-b� = a�-3a�b+3ab�-b�
============================================================