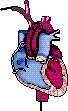 II.
The Heart
II.
The HeartI. Cardiovascular system
A. Components: Heart, arteries, veins, capillaries
B. Function: circulation provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removes wastes.
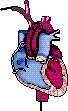 II.
The Heart
II.
The Heart
A. Location: in mediastinum behind sternum.
B. Coverings of the heart
1. Fibrous pericardium2. Serous pericardium
C. Heart wall layers
1. Epicardium2. Myocardium
3. Endocardium
D. Chambers
1. Atria2. Ventricles
3. Valves
a. Cuspid valves1. Tricuspid valve: RA/RV2. Bicuspid (mitral) valve: LA/LV
b. Semilunar valves
E. Cardiac Cycle
1. Atrial walls contract (atrial systole) while ventricular walls are relaxed (ventricular diastole).2. Atrial walls are relaxed (atrial diastole) while ventricular walls contract (ventricular systole).
3. Passage of blood through the heart: RA- right AV valve- RV-pulmonary SLV- pulmonary trunk- right and left pulmonary arteries- lungs-pulmonary veins- LA- left AV valve- LV- aortic SLV- aorta- body- superior and inferior vena cava- RA
F. Cardiac Conduction System
1. SA node: (sinoatrial node) the pacemaker.2. AV node: (atrioventricular node)
3. AV bundle: (atrioventricular bundle)
4. Purkinje fibers
III. Blood Vessels
A. General Structure
1. Tunica intima2. Tunica media
3. Tunica adventitia
![]() B.
Artery: carries blood away from heart.
B.
Artery: carries blood away from heart.
C. Vein: carries
blood toward heart. ![]()
D. Capillaries: carry blood from arterioles to venules.
E. Hepatic Portal Circulation
1. veins of spleen, stomach, pancreas, gall bladder, intestines send blood to liver before entering inferior vena cava.2. gastric, pancreatic, superior and inferior mesenteric veins empty into splenic vein.
3. empty into hepatic portal vein, formed by the union of the splenic and mesenteric veins.
4. drained from liver by hepatic veins, joining inferior vena cava.
F. Fetal circulation
1. Two umbilical arteries carry blood to placenta.2. Placenta allows for the exchange.
3. Umbilical vein returns oxygenated blood from placenta.
4. Ductus venosus serves as a detour and drains into inferior vena cava.
5. Foramen ovale: opening in the septum between RA and LA.
6. Ductus arteriosus: connects pulmonary artery with descending aorta.
IV. Blood Pressure
A.The force exerted by blood against the inner walls of the blood vessels.
1. Systole: maximum pressure during ventricular contraction. normal: 120 mm Hg2. Diastole: lowest pressure during ventricular relaxation. normal: 80 mm Hg.
B. Pulse: expanding, recoiling of arterial wall with contraction of ventricle.
C. Factors affecting blood pressure
1. Stroke volume: amount of blood discharged from ventricle with each contraction.2. Cardiac output: volume of blood pumped out of ventricle per minute.
3. Blood volume: directly proportional to blood pressure.
4. Peripheral resistance: friction between blood and walls of vessels.
5. Viscosity: ease with which molecules in liquid slide past each other.
D. Starling’s law of the heart: within limits, the longer or more stretched the heart fibers are at the beginning of contraction, the stronger their contraction.
E. Venous Blood Flow: blood moved by pressure of skeletal muscles, respiratory movements.
V. Paths of Circulation
A. Pulmonary Circuit: heart to lungs to heart.
B. Systemic Circuit: heart to body to heart.
VI. Pulse
A. Pulse points
1. Radial artery: wrist2. Temporal artery: in front of ear.
3. Common carotid artery: anterior edge of sternocleidomastoid at level of lower margin of thyroid cartilage.
4. Facial artery: lower margin of lower jawbone.
5. Brachial artery: bend of elbow along inner margin of biceps.
6. Popliteal artery: behind knee.
7. Posterior tibial artery: behind medial malleolus.
8. Dorsalis pedis artery: on dorsum of foot.
B. Pressure points
1. Temporal artery2. Facial artery
3. Common carotid artery: pressure against spinal column.
4. Subclavian artery: behind medial third of clavicle, pressing against first rib.
5. Brachial artery: above elbow on inside of arm. press against humerus.
6. Femoral artery: middle of groin where artery passes over pelvic bone.