![]()

This simulation shows the results of light striking a concave mirror which is also known a converging mirror. Notice that the light comes in parallel to principle axis of the mirror (not shown). As a result, the light gets reflected through the focal point of the mirror. The focal point is, by definition, where the light rays cross after coming in parallel to the principal axis. So for this mirror the focal point is where the five light "particles" overlap. This overlap would occur whether light is considered to be a particle or a wave.
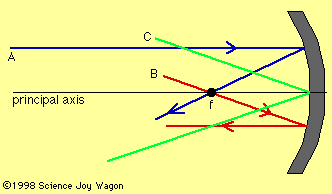
The following rules apply to light rays striking a concave (converging) mirror:
| A) Any ray coming in parallel to the principal axis gets reflected through the focal point (f). | |
| B) Any ray passing through or seeming to pass through the focal point (f) gets reflected parallel to the principal axis. | |
| C) Any ray striking the point where the principal axis touches the mirror will be reflected at an equal angle on the opposite side of the principal axis. |
©1998 Science Joy Wagon