This distance in lineal way will be the difference between separation and diameter of atoms. ( Separation-Diameter) .
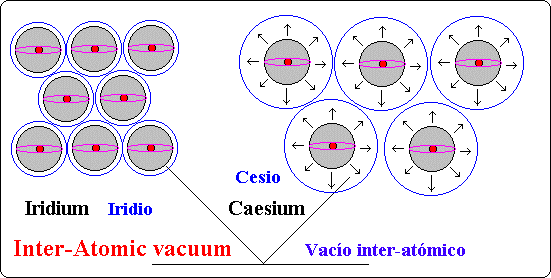
So much separation among atoms as their inter-atomic vacuum are propitiated by the magnetic and gravity fields.
Gravity field influence in the saturation of layers and in the separation of atoms (and inter-atomic vacuum), being great this vacuum in positions next to the saturation values. (2,10, 18, 36, 54, 86 ).
Magnetic fields create atomic orbits and build and support dimensions of atoms (diametre), and fit each electron in its orbit.
Inter-atomic vacuum seem to be mantained in the saturation of layer, He, Ne, ClH, OH2, NH3.
Although in the atomic bonds, inter-atomic vacuum disappears for bulding these atomic bonds.
---Inter-atomic vacuum also influences in the crystalline or amorphous states:
When a element has a lot of inter-atomic vacuum its state is more amorphous.
When a element has little inter-atomic vacuum its state is more crystalline breaking easily.
This is due to when atoms are near among them, they have to aling themselves
following the N-S direction of each atom.
When atoms are far ones from other, they already don't have to mantain this static position due to here the magnetic fields are more weak.