![]()
Glossary of Population Terms
Select the first letter of the word from the list above to connect to the appropriate section of the glossary.
- A -
Age-Sex Pyramid A bar chart, arranged vertically, that shows the distribution of a population by age and sex. By convention, the younger ages are at the bottom, with males on the left and females on the right.Also known as a population pyramid.
Age-Sex Structure The composition of a population as determined by the number or proportion of males and females in each age category. The age-sex structure of a population is the cumulative result of past trends in fertility, mortality, and migration. Information on age-sex composition is essential for the description and analysis of many other types of demographic data.
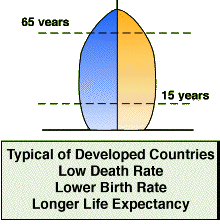
Aging Population A process in which the proportions of adults and elderly increase in a population, while the proportions of children and teenagers decrease. This process results in a rise in the median age of the population. This is occurring in New Zealand, where the median age of the population has risen from x to x.Aging occurs when fertility rates decline while life expectancy remains constant or improves at the older ages.
An aging population has a sge-sex pyramid with a broad middle and top, and a narrow base:
- B -
Baby Boom A dramatic increase in fertility rates and in the absolute number of births that occurred in New Zealand and other Western countries (including Japan) during the period following World War II (1947-1961).
Birth Control Practices employed by couples that permit sexual intercourse with reduced likelihood of conception and birth. The term birth control is often used synonymously with such terms as contraception, fertility control, and family planning.
Birth Rate (or crude birth rate) The number of live births per 1,000 population in a given year. Not to be confused with the growth rate.
Brain Drain The emigration of a significant proportion of a country's highly skilled, highly educated professional population, usually to other countries offering better economic and social opportunity. Examples young, better educated New Zealanders leaving for Australia in times when the Australian economy is performing better than the Neww Zealand economy.
- C -
Census A canvass of a given area, resulting in an enumeration of the entire population and often the compilation of other demographic, social, and economic information pertaining to that population at a specific time. See also survey.
Childbearing Years The reproductive age span of women, assumed for statistical purposes to be 15-44 or 15-49 years of age.
Cohort A group of people sharing a common temporal demographic experience who are observed through time. For example, the birth cohort of 1900 is the people born in that year. There are also marriage cohorts, school class cohorts, and so forth.
Crude Rate Rate of any demographic event computed for an entire population.
- D -
Death Rate (or crude death rate) The number of deaths per 1,000 population in a given year.
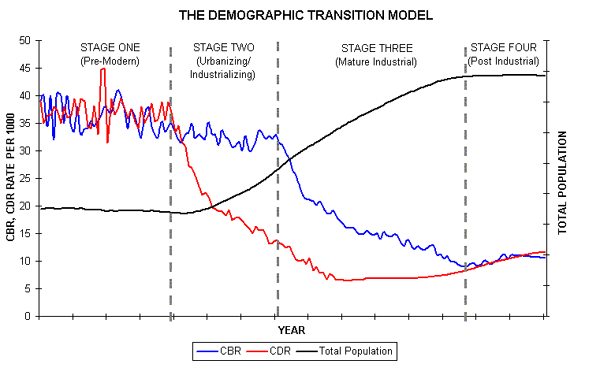
Demographic Transition The historical shift of birth and death rates from high to low levels in a population. The decline of mortality usually precedes the decline in fertility, thus resulting in rapid population growth during the transition period.
Demography The scientific study of human populations, including their sizes, compositions, distributions, densities, growth, and other characteristics, as well as the causes and consequences of changes in these factors.
Dependency Ratio The ratio of the economically dependent part of the population to the productive part; arbitrarily defined as the ratio of the elderly (ages 65 and older) plus the young (under age 15) to the population in the working ages (ages 15-64).
Doubling Time The number of years required for the population of an area to double its present size, given the current rate of population growth.
- E -
Emigration The process of leaving one country to take up permanent or semipermanent residence in another.
Ethnicity The cultural practices, language, cuisine, and traditions — not biological or physical differences — used to distinguish groups of people.
Family PlanningThe conscious effort of couples to regulate the number and spacing of births through artificial and natural methods of contraception. Family planning connotes conception control to avoid pregnancy and abortion, but it also includes efforts of couples to induce pregnancy.
Fertility Rate The number of live births per 1,000 women ages 15-44 or 15-49 years in a given year.
- G -
Gross National Income in Purchasing Power Parity (GNI PPP) Per Capita GNI PPP per capita is gross national income in purchasing power parity divided by midyear population. GNI PPP refers to gross national income converted to “international” dollars using a purchasing power parity conversion factor. International dollars indicate the amount of goods and services one could buy in the United States with a given amount of money.
Growth Rate The number of people added to (or subtracted from) a population in a year due to natural increase and net migration expressed as a percentage of the population at the beginning of the time period.
![]()
- H -
Household One or more persons occupying a housing unit.
- I -
Immigration The process of entering one country from another to take up permanent or semipermanent residence.
Immigration Rate The number of immigrants arriving at a destination per 1,000 population at that destination in a given year.
Infant Mortality Rate The number of deaths of infants under age 1 per 1,000 live births in a given year.
In-migration The process of entering one administrative subdivision of a country (such as a province or state) from another subdivision to take up residence.
- L -
Less Developed Countries Less developed countries (or regions) refer to countries in Africa, Asia (except Japan), Latin America and the Caribbean, and the islands of the Pacific (except Australia and New Zealand).
Life Expectancy The average number of years a person could expect to live.
- M -
Mean Age The average age of all the members of a population.
Median Age The age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older.
Metropolitan Area A large concentration of population, usually an area with 100,000 or more people. The area typically includes an important city with 50,000 or more inhabitants and the administrative areas bordering the city that are socially and economically integrated with it.
Migration The movement of people across a specified boundary for the purpose of establishing a new or semipermanent residence. Migration is divided into international migration (migration between countries) and internal migration (migration within a country). Migration is the result of push and pull factors. Push factors are those which force a person to move, while Pull factors are those which encourage a person to move to a particular destination.
Mobility The geographic movement of people.
More Developed Countries Following United Nations' definitions, "more developed countries," or industrialized countries (or regions), include Europe (including all of Russia), the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan.
Mortality Deaths as a component of population change.
- N -
Natural Increase (or Decrease) The surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths in a population in a given time period.

Net Migration The net effect of immigration and emigration on an area's population in a given time period, expressed as an increase or decrease.
- O -
"Old" Population A population with a relatively high proportion of middle-age and elderly persons, a high median age, and thus a lower growth potential.
Out-migration The process of leaving one subdivision of a country to take up residence in another.
- P -
Population A group of objects or organisms of the same kind.
Population Control A broad concept that addresses the relationship between fertility, mortality, and migration, but is most commonly used to refer to efforts to slow population growth through action to lower fertility. It should not be confused with family planning. See also family planning.
Population Density Population per unit of land area; for example, people per square mile or people per square kilometer of arable land.
Population Distribution The patterns of settlement and dispersal of a population.

"Population Explosion" (or "Population Bomb") Expressions used to describe the 20th century worldwide trend of rapid population growth, resulting from a world birth rate much higher than the world death rate.
Population Increase The total population increase resulting from the interaction of births, deaths, and migration in a population in a given period of time.
Population Momentum The tendency for population growth to continue beyond the time that replacement-level fertility has been achieved because of the relatively high concentration of people in the childbearing years.
Population Policy Explicit or implicit measures instituted by a government to influence population size, growth, distribution, or composition.
Population Projection Computation of future changes in population numbers, given certain assumptions about future trends in the rates of fertility, mortality, and migration. Demographers often issue low, medium, and high projections of the same population, based on different assumptions of how these rates will change in the future.
Pull Factors Pull factors are factors which encourage people to migrate to a parrticular destination. These are factors in the destination that exert a positive attraction or pull (such as a higher standard of living, more job or educational opportunities, greater tolerance of people's differences).
Push Factors Push factors are those which force a person to migrate from one palce to another. A range of circumstances at the place of origin (such as poverty, drought, famine, lack of jobs, over-population and civil war) repel or push people out of that place to other places.
- R -
Race Race is defined primarily by society, not by genetics, and there are no universally accepted categories.
Rate of Natural Increase (or Decrease) The rate at which a population is increasing (or decreasing) in a given year due to a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths, expressed as a percentage of the base population.
Reproductive Age See childbearing years.
- S -
Sex Ratio The number of males per 100 females in a population.
Stable Population A population with an unchanging rate of growth and an unchanging age composition as a result of age-specific birth and death rates that have remained constant over a sufficient period of time.
- T -
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) The average number of children that would be born alive to a woman (or group of women) during her lifetime if she were to pass through her childbearing years conforming to the age-specific fertility rates of a given year. This rate is sometimes stated as the number of children women are having today. See also gross reproduction rate and net reproduction rate.
- U -
Urban Countries differ in the way they classify population as 'urban' or 'rural.' Typically, a community or settlement with a population of 2,000 or more is considered urban.
Urbanisation Growth in the proportion of a population living in urban areas.
- V -
Vital statistics Demographic data on births, deaths, fetal deaths, marriages and divorces.
- Y -
"Young" or "Youthful" Population A population with a relatively high proportion of children, adolescents, and young adults; a low median age; and thus a high growth potential. The age-sex pyramid of a young or youthful population has a broad base and narrow top:

- Z -
Zero population growth A population in equilibrium, with a growth rate of zero, achieved when births plus immigration equal deaths plus emigration.