-
Symbol Defintion
Sqr(x) = Square root of x
Q01. Find signs and zeros of y' and y"
Diagram
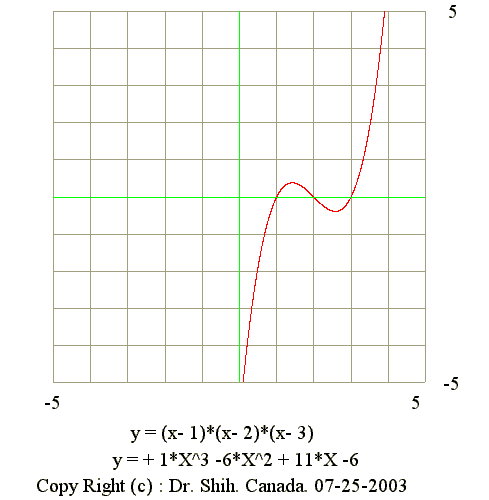
- 1. From the curve find the signs of y'
- y' = (+) if x LT x1 (Curve is increasing)
- y' = (0) if x EQ x1 (Maximum)
- y' = (-) if x between x1 and x2 (Curve is decreasing)
- y' = (0) if x EQ x2 (Minimum)
- y' = (+) if x GT x2 (Curve is increasing)
- 2. From the curve find the signs of y"
- y" = (-) if x LT x3 (Concave doweward)
- y" = (0) if x EQ x3 (Estimate the point of infletion)
- y" = (+) if x GT x3 (Concave upward)
- 3. Estimate the value of x1, x2 and x3 from the diagram
Go to Begin
Q02. Describe the curve y = (x - 1)/(x + 1)
Diagram
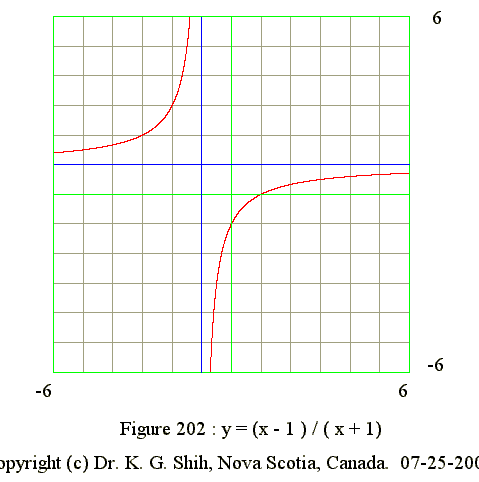
- Equation of vertical asymptote : x = -1 and y goes to infinite
- Equation of hoizontal asymptote : y = 1 as x tends to infinite
- No maximum point
- No minimum point
- No point of inflection
- y' = (+) : Domain is from -infinite to -1
- y' = (+) : Domain is from -1 to infinite
- y" = (+) : Domain is from -infinite to -1
- y" = (-) : Domain is from -1 to infinite
Go to Begin
Q03. y = (x^2 - 1)/(x^2 + 1)
Diagram
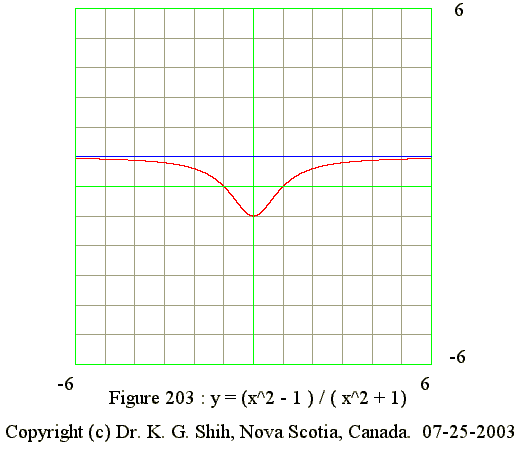
- Equation of vertical asymptote : None
- Equation of hoizontal asymptote : y = 1 as x tends to infinite
- No maximum point
- Minimum point is at (0, -1)
- Points of inflection : (-1,0) and (1,0)
- y' = (-) : Domain is from -infinite to 0
- y' = 0 when x = 0
- y' = (+) : Domain is from 0 to infinite
- y" = (-) : Domain is from -infinite to -1
- y" = 0 when x = -1 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (+) : Domain is between -1 and 1
- y" = 0 when x = +1 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (-) : Domain is from +1 to infinite
Go to Begin
Q04. y = (x^3 - 1)/(x^3 + 1)
Diagram
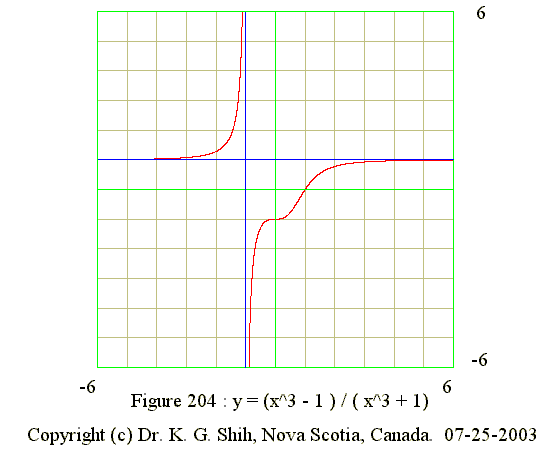
- Equation of vertical asymptote : x = -1
- Equation of hoizontal asymptote : y = 1 as x tends to infinite
- No maximum point
- No Minimum point
- Points of inflection : (0,-1) and (1,0)
- y' = (+) : Domain is from -infinite to -1
- y' = (+) : Domain is from -1 to infinite
- y" = (+) : Domain is from -infinite to -1
- y" = (-) : Domain is form -1 to 0
- y" = 0 when x = 0 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (+) when x is betwee 0 and 1
- y" = 0 when x = 0 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (-) : Domain is from +1 to infinite
Go to Begin
Q05. Describe the curve of y = (x^3 + 1)/(x^3 - 1)
Diagram
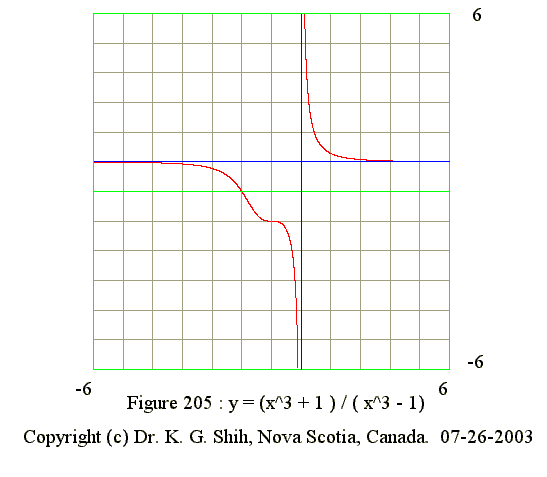
- Equation of vertical asymptote : x = 1
- Equation of hoizontal asymptote : y = 1 as x tends to infinite
- No maximum point
- No Minimum point
- Points of inflection : (-1,0) and (0,-1)
- y' = (-) : Domain is from -infinite to +1
- y' = (+) : Domain is from +1 to infinite
- y" = (-) : Domain is from -infinite to -1
- y" = 0 when x = -1 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (+) : Domain is form -1 to 0
- y" = 0 when x = 0 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (-) when x is betwee 0 and 1
- y" = 0 when x = 0 (point of inflextion)
- y" = (-) : Domain is from +1 to infinite
Go to Begin
Q06. Curve of y = x + 1/x
Diagram
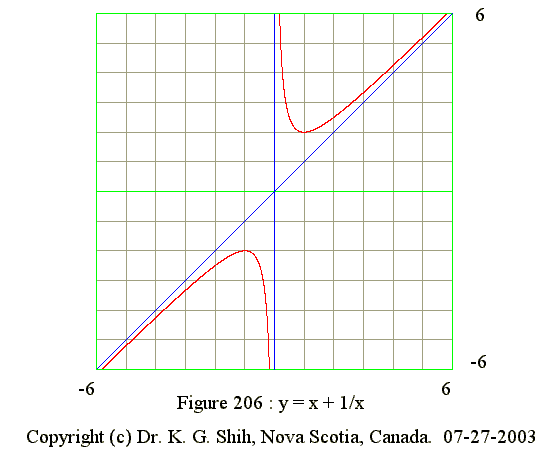
- x = 0 and y = infinite, hence x = 0 is vertical asymptote
- x = infinite and y = x, hence y = x is line asymptote
- Sketch lines : x = 0 and y = x
- y = x + 1/x
- y' = 1 - 1/(x^2) and y' = 0 when x = -1 or 1
- y' = (+) when x from -infinite to -1
- y' = 0 when x = -1 (Maximum point)
- y' = (-) when x between -1 and 0
- y' = (-) when x between 0 and 1
- y' = 0 when x = 1 (Minimum point)
- y' = (+) when x from 1 to infinite
- y" = 2/x^3
- y" has no zeros and no point of inflexion
- y" = (-) when x from -infinite to 0 (Curve concave downward)
- y" = (+) when x from 0 to infinite (Curve concave upward)
Go to Begin
Q07. Curve of y = x^2 + 1/x
Diagram
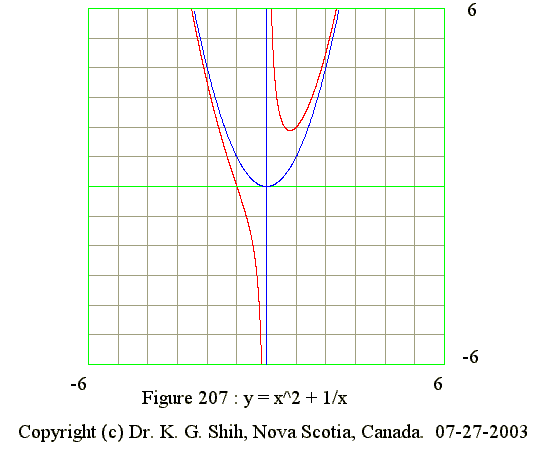
- x = 0 and y = infinite, hence x = 0 is vertical asymptote
- x = infinite and y = x, hence y = x^2 is parabola asymptote
- y = x^2 + 1/x
- y' = 2*x - 1/(x^2) and y' = 0 when x = -1 or 1
- y' = (-) when x from -infinite to 0
- y' = (-) when x from 0 to x1 (x1 = 0.707)
- y' = 0 when x = x1 (Minimum point)
- y' = (+) when x from x1 to infinite
- y" = 2 + 2/x^3
- y" has zero when x = -1 (point of inflexion)
- y" = (+) when x from -infinite to -1 (Curve concave upward)
- y" = (-) when x from -1 to 0 (Curve concave downward)
- y" = (+) when x from 0 to infinite (Curve concave upward)
Go to Begin
Q08. Sketch y = x^3 + 1/x
Diagram
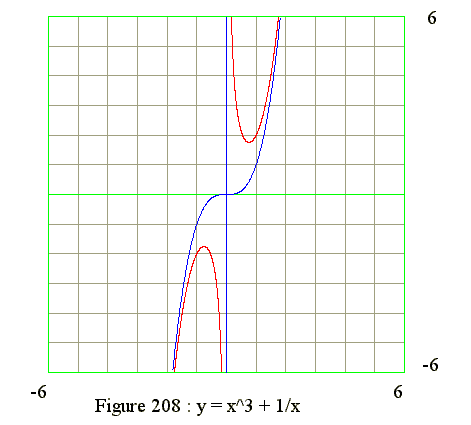
- x = 0 and y = infinite, hence x = 0 is vertical asymptote
- x = infinite and y = x, hence y = x^2 is parabola asymptote
- y = x^3 + 1/x
- y' = 3*x^2 - 1/(x^2) and y' has two zero
- y' = (+) when x from -infinite to x1 (x1 = -0.57735)
- y' = 0 when x = x1 (Maximum point)
- y' = (-) when x from x1 to 0
- y' = (-) when x between 0 and x2 (x1 = +0.57735)
- y' = 0 when x = x2 (Minimum point)
- y' = (-) when x between 0 and 1
- y' = (+) when x from 1 to infinite
- y" = 6*x +2/x^3
- y" has no zeros and no point of inflexion
- y" = (-) when x from -infinite to 0 (Curve concave downward)
- y" = (+) when x from 0 to infinite (Curve concave upward)
Go to Begin
Q09. Signs of y' and y" of y = (x - 1)^2/(2*x) Diagram to find signs of y' and y"
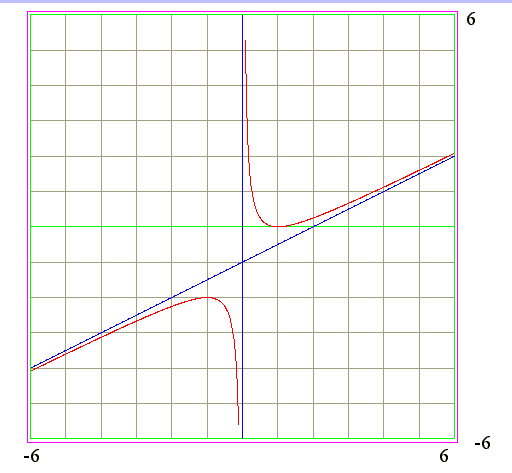
Go to Begin
Q10. From the graph of y = (x - 1)^3/(2*x) find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
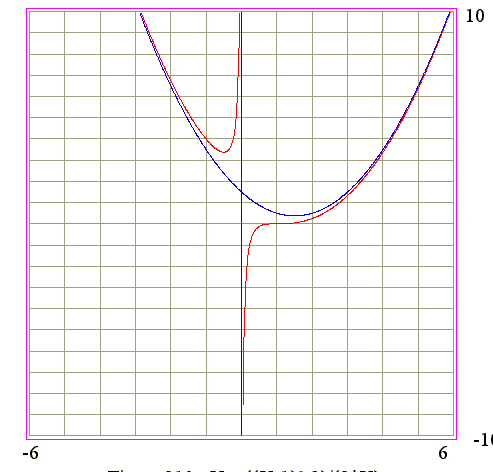
- 1. y-intercept
- 2. Zeros of y
- 3. Expression of function
- 4. Find domain if y is positive
- 5. Find domain if y is negative
- 6. Find domain if y' is positive
- 7. Find domain if y' is negative
- 8. Find domain if y' is zero
- 9. Find domain if y" is positive
- 10 Find domain if y" is negative
- 11 Find domain if y" is zero
- 1. y = -6 (= -product of roots) when x = 0
- 2. y = 0 if x = 1, x = 2 and x = 3
- 3. Expression : y = a*x^3 + b*x^2 + c*x + d and d = -6
- x = 1 and y = 0 hence 0 = 1*a + 1*b + 1*c - 6 .... (1)
- x = 2 and y = 0 hence 0 = 8*a + 4*b + 2*c - 6 .... (2)
- x = 3 and y = 0 hence 0 =27*a + 9*b + 3*c - 6 .... (3)
- Solve (1), (2) and (3) we have a = 1 and b = -6 and c = 11
- Hence the answer is y = x^3 - 6*x^2 + 11*x - 6
- 4. y is positive when x between 1 and 2 or x GT 3
- 5. y is negative when x between x = 2 and x = 3 of x LT 1
- 6. When x LT 1.5 or x GT 2.5 the curve is increasing. Hence y' is positive
- 7. When x between 1.5 and 2.5 the curve is decreasing. Hence y' is negative
- 8. When x = 1.5 or x = 2.5 the curve has minimum and y' = 0
- 9. The curve is concave upward when x GT 2 and hence y" GT 0
- 10 The curve is concave downward when x LT 2 and hance y" no negative value
- 11 The curve changel concavity at x = 2 and hence y" is zero (point of inflexion)
Go to Begin
Q11. From the graph of y = (x - 1)^4/(2*x) find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
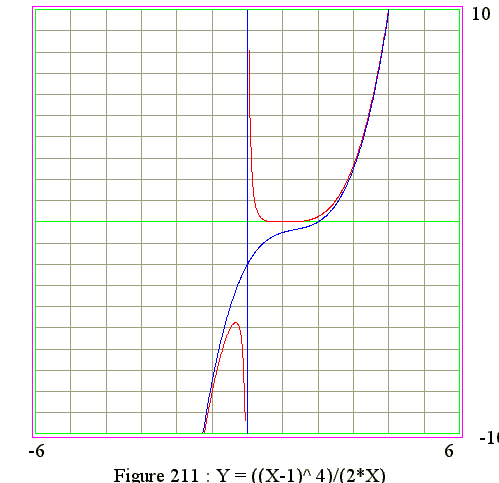
- 1. y-intercept
- 2. Zeros of y
- 3. Expression of function
- 4. Find domain if y is positive
- 5. Find domain if y is negative
- 6. Find domain if y' is positive
- 7. Find domain if y' is negative
- 8. Find domain if y' is zero
- 9. Find domain if y" is positive
- 10 Find domain if y" is negative
- 11 Find domain if y" is zero
- 1. y = 0 when x = 0
- 2. y = 0 if 2*pi, -pi, 0, pi and 2*pi
- 3. Expression : y = sin(x)>
- 4. y is positive when x between -2*pi and -pi or x between 0 and pi
- 5. y is negative when x between -1*pi and 0 or x between pi and 2*pi
- 6. y is positive when x curve is increasing
- x between -2.0*pi and -1.5*pi
- x between -0.5*pi and +0.5*pi
- x between +1.5*pi and +2.0*pi
- 7. y is negative when curve is decreasing
- x between -1.5*pi and -0.5*pi
- x between +0.5*pi and +1.5*pi
- 8. When x = -1.5*pi or x = -0.5*pi or x = 0.5*pi or x = 1.5*pi then y' = 0
- 9. The curve is concave upward when
- x between -pi and 0 >li> x between pi and 2*pi
- 10 The curve is concave downward when
- x bewteen -2*pi and -pi
- x between 0 and pi
- x = -pi
- x = 0
- x = pi
Go to Begin
Q12. From the graph of y = x^2 - 6*x + 8 find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
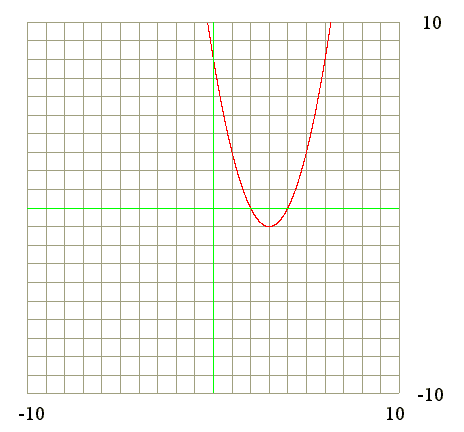
Go to Begin
Q13. From the graph of y = cubic function find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
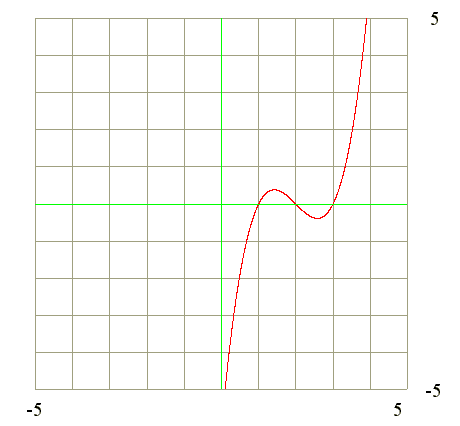
Go to Begin
Q14. Construct parabola geomtrically
Diagram
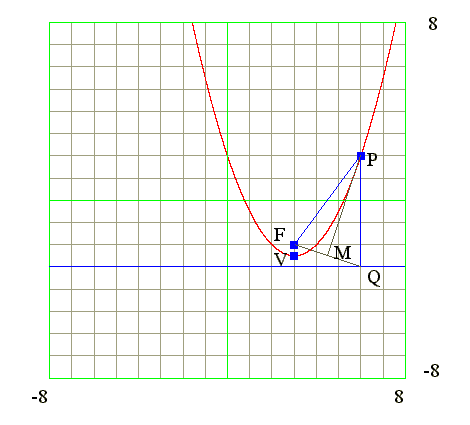
- 1. Find focus and equation of directrix
- 2. Draw focus F, principal axis and directrix
- 3. Draw a line perpendicular to directrix at Q1
- 4. Join F and Q1
- 5. Draw bisector of FQ1 and meet the line at P1
- 6. P1 is point on parabola (FP1 = FQ1)
- 7. Repeat steps 3 to 6 to get more points P2, P3, ....
- 8. Draw smooth curve passing p1, p2, p3, ....
Go to Begin
Q15. dA = (r^2)*cos(U)*dr*dV*dU
Diagram
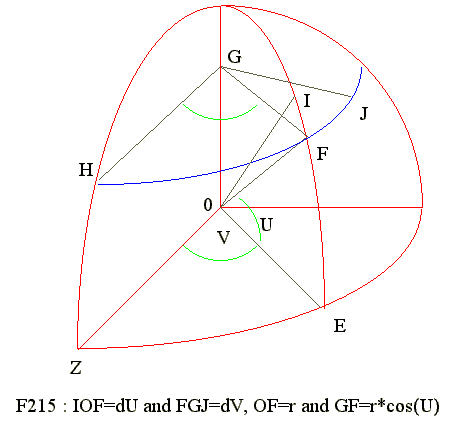
- See CA 09 06
Go to Begin
Q16. From the graph of y = sin(x) find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
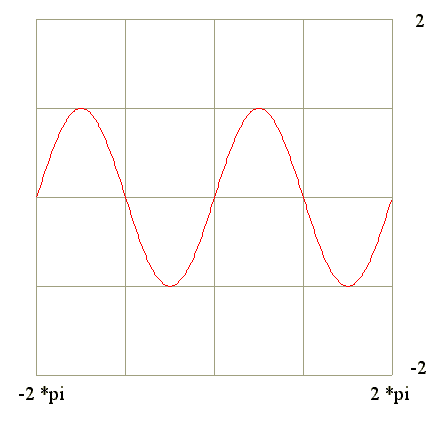
Go to Begin
Q17. From the graph of y = (x^3)/(x^2 - 1) find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
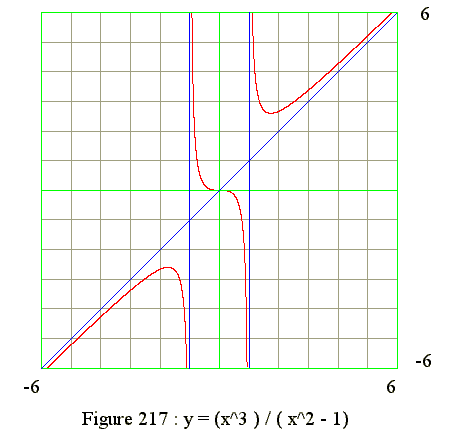
- 1. x = -1
- 2. x = +1
- 3. y = x
- Domins for signs of y
- 1. If x LT -1, then y = (-) with maximum
- 2. If x between -1 and 1, y = (-).
- 3. If x GT 1, then y = (+) with minimum
- Domins for signs of y'
- 1. If x LT -1, then
- y' = (+) to maximum point
- y' = 0 at maximum point
- y' = (-) from maximum to x = -1
- 2. If x between -1 and 1, then y' = (-)
- 3. If x GT 1, then
- y' = (-) to minimum point
- y' = 0 at minimum point
- y' = (+) after minimum point
- 1. If x LT -1, then
- Domins for signs of y"
- 1. If x LT -1, then y" = (-) : Curve is concave downward
- 2. If x Between -1 and 0, then y" = (+) : Curve concave upward
- 3. If x EQ 0, then y" = 0 : Point of inflection
- 4. If x between 0 and 1, y" = (-) : Curve is concave downward
- 5. If x GT 1, then y" = (+) : Curve concave upward
- 1. Draw asymptotes
- 2. If x is less then -1
- y is negative
- As x from -infinite to -1, y from -infinite to maximum to -infinite
- Hence curve is between y = x and x = -1
- Hence curve is concave downward with a maximum point (y' = 0)
- 3. If x is between -1 and 0
- y is positive
- y is from infinite to 0
- y is concave upward
- 4. If x is between 0 and 1
- y is negative
- y is from 0 to -infinite
- y is concave downward
- 5. At x = 0, the curve has point of inflection (y" = 0)
- 6. if x is greater than 1
- y is positive
- As x from 1 to infinite, y from infinite to minimum to infinite
- Hence curve is between y = x and x = 1
- Hence curve is concave upward with a minimum point (y' = 0)
- Finf y'
- y' = ((3*x^2)*(x^2 - 1) - (x^3)*2*x)/(x^2 - 1)^2
- y' = (3*x^4 - 3*x^2 - 2*x^4)/(x^2 - 1)^2
- y' = (x^4 - 3*x^2)/(x^2 - 1)^2
- If y' = 0, then x^4 - 3*x^2 = 0
- Hence x = 0 : It is point of inflection because y" = 0
- Hence x = -Sqr(3) : It if maximum becasue y" = (-)
- Hence x = +Sqr(3) : It if minimum becasue y" = (+)
- Find y"
- y" = ((4*x^3 - 6*x)*(x^2 - 1)^2 - 2*(x^2 - 1)*2*x*(x^4 - 3*x^2))/(x^2 - 1)^4
- y" = ((4*x^3 - 6*x)*(x^2 - 1) - 4*x*(x^4 - 3*x^2))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- y" = ((4*x^5 - 4*x^3 - 6*x^3 + 6*x - 4*x^5 + 12*x^3))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- y" = ((2*x^3 + 6*x))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- y" = 2*x*(x^2 + 3))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- Value of y"
- x = 0 and y" = 0 : Point of inflection
- x LT -1, then y" = (-)
- x GT +1, then y" = (+)
- Minimum
- y' = 0 and y" = (+)
- Hence x = Sqr(3) and y = (Sqr(3))^3/(Sqr(3))^2 -1)
- x = 1.732 and y = 2.59807
- Maximum
- y' = 0 and y" = (-)
- Hence x = -Sqr(3) and y = (-Sqr(3))^3/(Sqr(3))^2 -1)
- x = -1.732 and y = -2.59807
Go to Begin
Q18. From the graph of y = (x^4)/(x^2 - 1) find the signs of y' and y"
Diagram
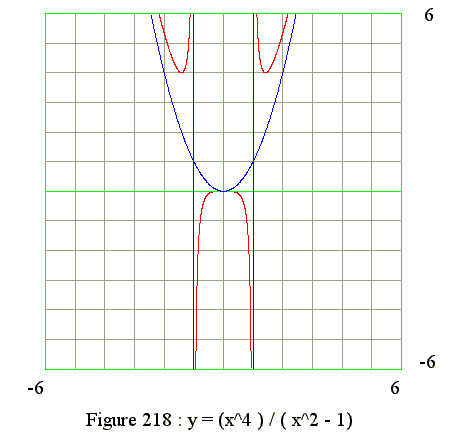
- 1. x = -1
- 2. x = +1
- 3. y = x^2
- 1. Draw asymptotes
- 2. If x is less then -1
- y is positive
- As x from -infinite to -1, y from infinite to minimum to infinite
- Hence curve is between y = x^2 and x = -1
- Hence curve is concave upward with a minimum point (y' = 0)
- 3. If x is between -1 and 0
- y is negative
- y is from -infinite to 0
- y is concave downward
- 4. If x is between 0 and 1
- y is negative
- y is from 0 to -infinite
- y is concave downward
- 5. At x = 0, the curve has maximum (y" = 0 ?)
- 6. if x is greater than 1
- y is positive
- As x from 1 to infinite, y from infinite to minimum to infinite
- Hence curve is between y = x^2 and x = 1
- Hence curve is concave upward with a minimum point (y' = 0)
- Finf y'
- y' = ((4*x^3)*(x^2 - 1) - ((x^4)*2*x)/(x^2 - 1)^2
- y' = (4*x^5 - 4*x^3 - 2*x^5)/(x^2 - 1)^2
- y' = (2*x^5 - 4*x^3)/(x^2 - 1)^2
- If y' = 0, then x^5 - 2*x^3 = 0
- Hence x = 0 : It is maximum point
- Hence x = -Sqr(2) : It if minimum becasue y" = (+)
- Hence x = +Sqr(2) : It if minimum becasue y" = (+)
- Find y"
- y" = ((10*x^4 - 12*x^2)*(x^2 - 1)^2 - 2*(x^2 - 1)*2*x*(2*x^5 - 4*x^3))/(x^2 - 1)^4
- y" = ((10*x^4 - 12*x^2)*(x^2 - 1) - 4*x*(2*x^5 - 4*x^3))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- y" = ((10*x^6 - 10*x^4 - 12*x^4 + 12*x^2 - 8*x^6 + 16*x^4))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- y" = ((2*x^6 - 6*x^4 +12*x^2))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- y" = 2*x^2*(x^4 - 3*x^2 + 6))/(x^2 - 1)^3
- Value of y"
- x = 0 and y" = 0 : Not agree with diagram. Why ?
- x LT -1, then y" = (+)
- x GT +1, then y" = (+)
- Maximum
- y' = 0 and y" = (-)
- Hence x = Sqr(2) and y = (Sqr(2))^4/(Sqr(2))^2 -1)
- x = 1.414 and y = 4
- Maximum
- y' = 0 and y" = (-)
- Hence x = -Sqr(2) and y = (-Sqr(2))^4/(Sqr(2))^2 -1)
- x = -1.414 and y = -4
Go to Begin
