
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
- Network topology refers to the layout of the computers and devices in a communication and devices in a communications network.
- PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY- The configuration of cables, computers and other peripheral
- LOGICAL TOPOLOGY- the path that travels between computers on a network
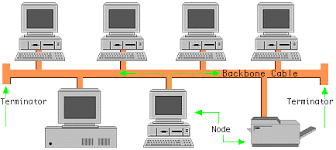
| BUS TOPOLOGY |
RING TOPOLOGY |
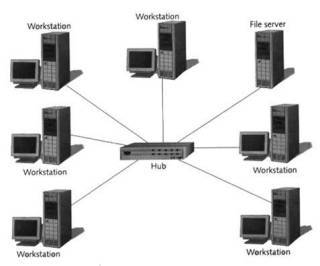
STAR TOPOLOGY |
|
| DIAGRAM |
 |
 |
 |
| PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY |
A bus network consists of a single central cable (backbone/trunk) to which all computers and other devices connect(node). |
A cable forms a closed loop(ring) with all computers and devices arranged along the ring. |
All computers and other device on network connect to a central device(hub/switch), thus forming a star. |
| LOGICAL TOPOLOGY |
In a bus network, it
transmit data, instructions and information (the address of the
receiving device is included) as a series of signal in both
directionwhere all nodes receive the signal but only intended recepient
will accept the signal |
Data
transmitted on a ring network travels from device to device around the
entire ring, in one direction until it reach its destination by using
token |
In star network, data instructions and informations transfer from one node to another node passes through hub/switch |
| ADVANTAGES |
|
|
|
| DISADVANTAGES |
|
|
|
