| HOME | NETWORK ARCHITECTURE | NETWORK TOPOLOGY | CLASSIFICATION OF NETWORK | INTERNET | INTERNET SERVICES |
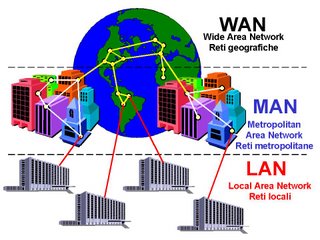
The main differentiation among these classifications is their area of coverage (distinguish by the geographical area each network serves).
|
Classification of Network |
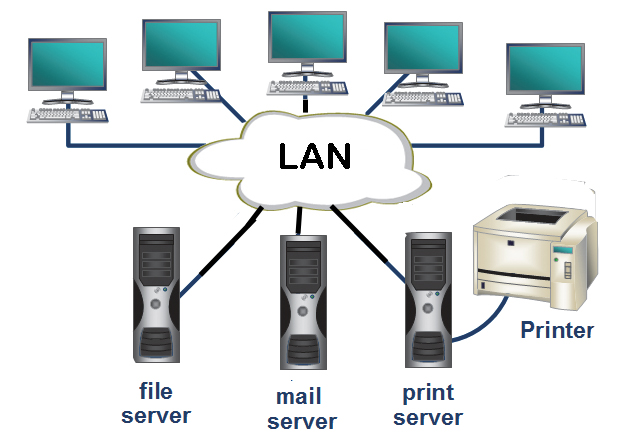
Local Area Network (LAN)
|
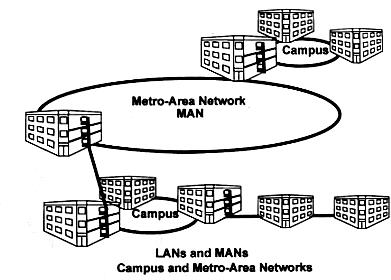
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
|
Wide Area Network (WAN)
|
|
Definition |
A
network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area. |
A
high-speed network that connects local area networks (LANs) in a metropolitan
area. |
A
network that covers a large geographical area. |
|
Areas of
coverage |
LANs
located within the same building such as home, school computer laboratory,
office building. |
MANs
connect various locations such as campuses, offices and government that are
frequently used as links between buildings.
|
WANs
located within a countryside and worldwide networks, using a communications
channel that combines many types of media such as telephone lines, cables and
radio waves. The internet is the world’s largest WAN. |
|
Ownership |
LANs
are owned and operated by individual organizations. |
MANs
are owned by a group of users who jointly own and operate the network. |
WANs
have no ownership. (Anybody can connect to the internet.) |
|
Distance |
LANs
span distance less than a mile. |
MANs
span over distance up to 100 miles (161km). |
WANs
span distance greater than 100 miles. |
|
Example of
Network |
Personal Area Network (PAN): A type of
wireless network that works within a very small area your immediate
surroundings. A network personal devices for one individual such as digital
camera and mobile phones that designed to enable those devices to communicate
and share data. |
Campus Area Network (CAN): A type of a computer network interconnecting
a few local area networks (LANs) within a university campus or corporate
campus. |
Enterprise Private Network (EPN): A type
of network built by an enterprise to interconnect various company sites,
e.g., production sites, head offices, remote offices, shops, in order to
share computer resources. |
|
Advantages |
Hardware and
software can be shared. |
|
These
are similar to those LAN’s except the scale of sharing etc. becomes far
greater and can be world-wide. |
|
Disadvantages |
Printing
can be slow, long print queues may develop. |
|
Encryption
of secure data such as financial transactions is necessary because it is even
easier to capture data. |
|
Speed |
LAN
faster than MAN and WAN. |
MAN
faster than WAN but slower than LAN. |
WAN
slower than LAN and MAN. |