
School Information
Reference Materials
Information for Students
Problem of the Week
Chaparral & New Mexico
Math Tutorial
Marvelous Math Links
Odds & Ends
Games and Gadgets
Fraction Calculator
Weekly Skills Quiz
Famous Matematicians
Student of the Month
class. As time allows further definitions will be added.
Absolute Value
The absolute value of a number is written as |x|. It is the value of x
without regard to sign. (i.e. if x is positive the absolute value is x; if
x is negative, the absolute value is -x). It represents simply the quantity,
not the sign or direction.
The absolute value of +4 is 4 while the absolute value of -4 is also 4.
Acute Angle
An acute
angle
is an angle that is less than 90 degrees.
See also right and
obtuse angles.
Acute Triangle
An acute triangle is one in which all three of the interior
angles are less than 90 degrees,
or acute angles
Angle
An angle is formed by two rays l and m with a common end
point. l and m are called the sides of the angle and the common
point 'A' is the vertex. angles are usually labeled with small Greek letters,
in this case an ![]()
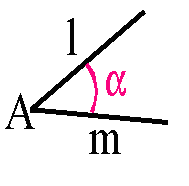
Area
Area is the number of square units that are contained in a figure. For rectanglular shapes it is found by multiplying the length and width. For a circle circle it is found by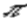 is about 3.14159.
is about 3.14159.
Average
A number found by adding two or more numbers and dividing by the number of numbers.For example: Jose had grades of 3, 4, 4, 3, and 2.
* His average is found by first adding his grades - 3+4+4+3+2=16.
* Then divide this total by the number of grades 16 divided by 5 gives an average of 3.2 for Jose's grade.
Capacity
The amount of liquid or other material a container may hold.Cartesian Coordinates
A system of locating points on a plane, or flat, surface such as a piece of paper. It was developed by René Descartes, a French mathematician. In this system the position of a point is determined by measuring along two perpendicular lines or axis.
When describing the location of a point the x-axis coordinate ALWAYS comes first followed by the y-axis coordinate. The two are separated by a comma and placed in parenthesis. thus in the above point A is described by the ordered pair (1,3). Point B is (2, 2.5). C is (3, 1.5). D is (-2, 2.5) and E is (-1, -2.5) What do you think the coordinates of F are?
If you said (3, -2) congratulations, you are correct.
Circle
A circle is the locus of all points that are equal distant from a point called the center. The radius is a line drawn from the center to the outside, or circumference, of the circle. The diameter is a line drawn from the circumference, through the center, through the circle and ending at the circumference on the other side of the circle.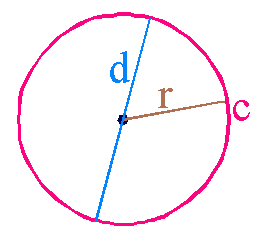
Circumference
Circumference is the distance around a circle. I t is found as shown below: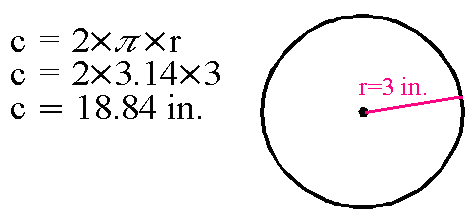
Common Factor
A number which is a factor of two or more numbers.Example: 2 is a factor of 6 and of 8 therefore it is a common factor of 6 and 8.
Common Multiple
A number which is a multiple of two or more numbers.Example: 12 is a multiple of 2 and 3. Also 6, 18, and 24 are common multiples of 2 and 3.
Congruent
Geometric figures or shapes are said to be congruent if one would fit exactly on top of the other. (i.e. They are the same shape and size)Degree
A degree is a measure of a circle. There are 360 degrees in a circle.Denominator
A denominator is the bottom number in a fraction.Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the center of the circle with endpoints on the circumference.

Difference
A difference is the answer to a subtraction problem.Distributive Law
The distributive law is an equlity relating addition and multiplication. It states that the result of adding two numbers and multiplying by a third is the same as multiplying the third by each of the others and then adding the results. In other words,Equivalent Fractions
Fractions which name the same quantity are equivalent fractions. Equivalent fractions will also reduce to the same fraction in lowest terms.Equilateral triangle A triangle in which all three sides are equal.
Euler's Theorom on Polyhedra
Euler discovered an important theorem relating the number of edges, surfaces, and vertices of a polyhedron. It is expressed with the equationv + s = e + 2, where e is the number of edges, s is the number of surfaces and v is the number of vertices.
Even Number
An integer that ends with a 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8. Even numbers are all evenly divisible by 2.See also Odd Numbers
Exponent
An exponent tells how many times to use the base number as a factor.Example:
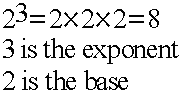
Factor
A factor of a given number is a number that will divide evenly into the given number. The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Factors that are prime numbers are very important in solving fraction problems.Factorial
For positive integers, the product of the first n numbers is called 'n-factorial'. It is written with an exclamation mark following the number. Thus, 3! is read as 3-factorial and is found by 1x2x3=6, 4!=1x2x3x4=24.Fraction
A fraction is a rational number expressed as the quotient of two integers, a numerator and a denominator.In addition, it describes how something is divided up. The denominator describes how many parts something is divided into. The numerator describes how many of these parts are of interest. Thus if a pizza is divided into 12 pieces and you were to eat 5 of them the amount of pizza you ate could be described with the fraction
Golden Section or Golden Ratio
The golden section is expressed by the below drawing.
Greatest Common Factor
The greatest (largest) number that is a factor of two or more other numbers. The number 12 has factors of 2, 3, 4, and 6. The number 18 has factors of 2, 3, 6, and 9. The greatest factor they share in common is 6.Heron's Formula
The ancient mathematician Heron discovered and interesting formula for the area of a triangle expressed as follows: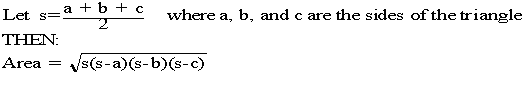
Inequality
If two expressions are related by one of the symbolsInteger
The set of integers includes the positive whole numbers, the negative whole numbers, and zero. When adding, subtracting and multiplying with integers the result is always and integer. However, dividing two integers may result in a non-integer referred to as a rational number.Irrational Number
An irrational number is one which may not be represented as the ratio of two rational numbers.Isosceles Triangle
A triangle with at least two equal sides is called an isosceles triangle.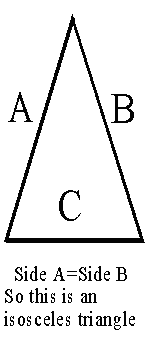
Least Common Denominator (LCD)
The least common denominator for a group of fractions is simply the least common multiple of their denominators. Since fractions may only be added if they have a common denominator, the ability to find and convert to a common denominator is important.Least Common Multiple
The least common multiple of a group of numbers is the smallest number that each member of the group will divide into evenly.Thus, for the numbers 2, 3, and 4, the smallest number they each divide into evenly is 12. Thus 12 is the LCM of 2, 3, and 4.
Line
A never ending straight path.Line Segment
A part of a line with definite endpoints.Mean
Another name for an average.Median
The median of a group of numbers is the value which has an equal number of numbers greater and less than its value. The median value of 4, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 9 is 6 since there are 4 values greater than 6 and 4 values less than 6.Meter
The basic unit of the metric measuring system. It is approximately equal to 39.37 inches or a little over a yard.Mixed Number
A mixed number is the sum of an integer and a common fraction. The addition sign is usually not written.
Mode
The number in a group of numbers that occurs most often.If Maria had grades of 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 2, 1, and 4, the mode would be 3 since that is the number that occurs most often.
Multiple
The multiple of a number is the number multiplied by a second number. Thus some multiples of 5 are 10, 15, and 20.5x2=10
5x3=15
5x4=20
Number Line
The number line is a straight line used to picture both positive and negative numbers. In addition it provides a visual representation of their absolute values.Numerator
A numerator is the top number in a fraction.Obtuse Angle
An obtuse angle is one that is larger than 90 degrees.Odd Number
An integer that ends with a 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9. Odd numbers are not evenly divisible by 2.See also Even Numbers
Ordered Pair
A pair of numbers that cvan be used to locate a point on a map, grid, or Cartesian Plane. In the orderd pair (2, 3) the 2 tells how far to the right of 0 while the 3 tells how many units up form 0.See also Cartesian Coordinates.
Order of Operations
Anyone faced with a prolem like this,My Multiply Dear Divide Aunt Add Sally Subtract
If there are parenthesis, do what is inside them first! Then replace the expression in the parens with the equivalent value.
Simply add the word 'please' to the beginning of the above aid to help you remember.
Please Parenthesis My Multiply Dear Divide Aunt Add Sally Subtract
Parallel
Two straight lines which lie in the same plane and do not intersect are said to be parallel.Parallelogram
A quadrilateral in which the pairs of opposite sides are parallel line segments is called a parallelogram.Pascal's Triangle
Pascal's triangle is illustrated below. each number is found by adding the two numbers above it. The outside numbers are always 1.
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
Percent
Percent simply means divided by 100. (35% means 35 divided by 100.)Perimeter
The distance around a figure. For a polygon, with straight sides, add the lenghts of all the sides.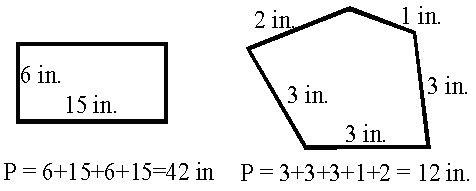
For a circle the perimeter is called the 'circumference' and is found by:
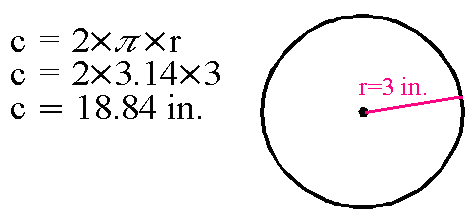
Perpendicular
Perpendicular means meeting at right angles. Lines that are perpendicular form right angles where they meet.Pi
The ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle, approximately equal to 3.14159265359. Some fractions that closely approximate pi are given below: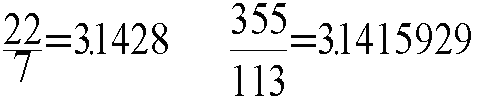
The mathematical symbol for Pi is:
Polygon
A closed plane figure with sides that are line segments. Two line segments meet at a vertex to form an angle.In a regular polygon all the sides are the same length.
| Polygon | Number of Sides |
| Triangle | |
| Quadrilateral | |
| Pentagon | |
| Hexagon | |
| Septagon | |
| Octagon | |
| Nonagon | |
| Decagon |
Plane
A plane is a flat surface passing through three points.Power
A power is the product of equal factors. The expressionIn this notation the 2 is called the base and the 3 is called the exponent.
Prime Number
A prime number is a number that has no factors other that one and itself. 5 is prime since only 1 and 5 will divide evenly into 5. 6 is not prime since it may be divided by 2 and 3 in addition to 1 and 6. Some of the first prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, and 31.Product
A product is the answer to a multiplication problem.Proportion
If two ratios are equal they form a proportion. The two fractions shown here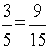 are equal, they may be reduced to identical fractions in lowest terms,
so they form a proportion.
are equal, they may be reduced to identical fractions in lowest terms,
so they form a proportion.
Quadrilateral
A polygon having four sides.Quotient
A quotient is the answer to a division problem.Radius
The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to the circumference. In the below diagram it is the brown line.
Range
The difference between the largest and the smallest in a group of numbers.Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are all numbers that may be written as a fraction. In other words they are all quotients of rational numbers.Ratio
The ratio of two quantities is simply their quotient. It is most often written as a fraction,For a ratio to exist both numbers must have no dimensional units or the same dimensional units such as a ratio of 2 miles to 8 miles. It does not make sense to have a ratio of 3 apples to 4 oranges!
See also proportion