MNR Spectrum
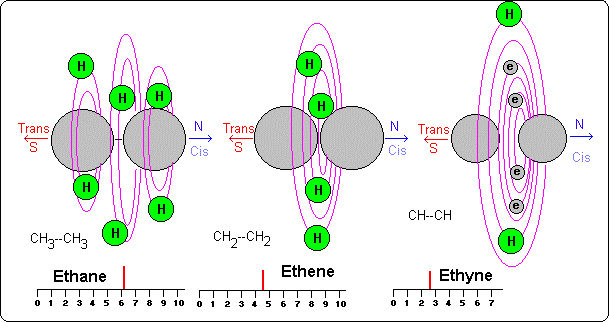
--Ethyne or acetylene that contains three covalent connections; one is supported by two hydrogen atoms and other two connections are carried out by four electrons given from the atoms of carbon (each one contribute two electrons).
In the acetylene we have drawn the two atoms of carbon a little smaller, what means that these atoms have lost part of their volume when giving electrons, and therefore, when giving particular orbits to form common orbits.
Nmr-Spectrum
The ethane Nmr that is of 6 ppm, and as we already said, this take place for combined resonance of all the atoms of hydrogen due to its special situation.
In the ethene the value is of 4.4 what would mean that the double connection makes close a little more the atoms of hydrogen and possibly (like in the ethane) to produce resonance jointly among them arriving to these values.
In the acetylene (2,5 ppm) when having single two atoms of hydrogen their frequency of resonance it would be smaller, but when having triple connections the carbons would be more together and they would produce bigger influence on the hydrogen atoms. Result: their frequency would be bigger than a methyl group (1,2) but smaller than a double connections of four hydrogen atoms (4,4), that is to say, its frequency is of 2.5.