NETWORK BASIC | NETWORK ARCHITECTURE | CLASSIFICATION OF NETWORK | WEB PAGE NAVIGATION | INTERNET SERVICE
Topic 3.0-INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
3.1 Network Basics:
3.1.2 Network Architecture
Introduction
Network architectures is the way network are designed to communicate.
Types of network architecture:
-Peer-to-peer (P2P)
-Client-Server
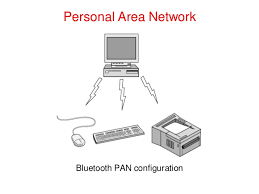
Peer-to-peer Network
Definition :
1. A network model in which all computers can function as
clients or servers as needed, and there’s no centralized
control over network resources.
2. Is a simple, inexpensive network that typically connects
fewer than 10 computers.
Most computers function as clients or servers.
Example : A computer can act as a server by sharing a printer it’s
connected to and at the same time act as client by accessing a file
shared by another computer on the network.
Peer-to-peer network diagram
Advantages of a peer-to-peer network:
Less startup cost to setup the network architecture - No need for a server.
Easy to Setup up - An operating system (such as Windows XP)
already in place may only need to be reconfigured for peer-to-peer
operations.
Disadvantages of a peer-to-peer network:
Decentralized - No central repository for files and applications.
Client-Server Network
Network in which one or more computers act as a
server, and the other computers (clients) on the network request
services from the server.
Computers connected together to create a network which fall into two categories: clients (workstations) and servers.
The Client - Computer on a network that requests resources from the server. Also called a workstation.
The Server - Computer that controls access to the hardware,
software, and other resources on a network, and provides a centralized
storage area for programs, data, and information.
Client-Server network diagram
Servers
Servers are special, powerful computers that provide ‘services’ to the client computers on the network.
These services might include:
Providing a central, common file storage area
Sharing hardware such as printers
Controlling who can or can’t have access the network
Sharing Internet connections
An architecture in which the user's PC (the client) is the requesting
machine, and the server is the supplying machine, both of which are
connected via a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN) such as the Internet.
Advantages of a Client/Server
Centralized - Resources and data security are controlled through the server.
Scalability - Any or all elements can be replaced individually as needs increase.
Flexibility - New technology can be easily integrated into system.
Interoperability - All components (client/network/server) work together.
Accessibility - Server can be accessed remotely and across multiple platforms.
Disadvantages of a Client/Server
Expense - Requires initial investment in dedicated server.
Maintenance - Large networks will require a staff to ensure efficient operation.
Dependence - When server goes down, operations will cease across the network