Aviation
I will like to define the term aviation as known worldwide and further go on to elaborate on the aircraft.
'Aviation is a word or term that includes all the activities involved in building and flying aircraft, especially airplanes.'
So you see, Aviation is much concerned with airplanes and I have decided to talk on airplanes.
Aircraft manufacturing Aircraft companies produces chiefly airplanes, but also manufacture gliders, helicopters, and parts for spacecraft. Countries like the United States of America, Great Britain , Canada and other European countries have thousands of factories responsible for the production of aircraft and other parts for spacecraft. Manufacturers produce three main types of airplanes:
General aviation activities These includes pleasure flying, land surveying, giving flying instructions, inspecting telephone lines, and scattering seeds and spraying crops. Another important general aviation activity is the use of light planes to provide transportation. Most air taxi services are small companies that operate a few light planes. Nevertheless, some of them have planes that can carry about 20 passengers.Some large airlines also provide air taxi service. Many businesses ave theri own light planes to fly officials and salespoeple to out-of-town assignments. Light planes are also used to carry cargo and passengers in areas of the world that lack highways or railroads. Airline operations Almost every country has at least one airline. Some are owned by the government and others are owned by the government. Ther are two main types of airline service- scheduled flights and non-scheduled flights. Scheduled flights are made over certain routes according to a timetable. Nonscheduled flights are mostly charter flights for customers who want to hire a plane to fly to a particular place at a particular time. In some countries like the USA, airlines must receive permission from the government to use commercial transport planes for scheduled flights. The airlines that the government approves for such flights are called certificated airlines. To receive government certification, an airline's planes and Pilots must meetgovernment standards. Certificated airlines that connect the nation's largets cities are called trunk airlines. Certificated airlines that serve smaller cities and towns are called local-service, or feeder airlines. Government approved airlines that make nonscheduled flights are called supplemental, or non scheduled, air carriers. Most airlines carry both passengers and cargo. Airliners usually carry a certain amount of freight on passenger flights. Airport Operations Airports provide the runways, navigation aids, and other ground facilities needed for air travel. The United States has more than 11,000 airports. A few of them have the facilities to andel large planes anyway. Others are small airfields that can serve only light planes. Cities or public corporations own most large airports. Some small airports are publicly owned, but most are private airfields owned by organizations or individuals. Aviation support industries They provide a wide variety of supplies and services to airlines, airports, pilots, and passengers. Some companies furnish repair services or fuel for airplane. Freight forwarders make arrangements for shiping air cargo. Various food services prepare meals to be served on passenger flights. Some insurance brokers specialize in flight insurance, and some lawyers specialize in air law. Private weather bureaus supply pilots with weather information not provided by government weather services.
Now to the topic Airplanes!.

How the Airplane Flies
These basic forces can be illustrated as:
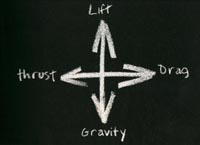 Well then, what is gravity? someone may want to know. Gravity is the natural force that pulls a plane towards the ground. Lift is the force that pushes a plane upward against the force of gravity. It is created by the movement of a plane's wing through the air. Drag is the natural force of air opposing an airplane's forward movement. Thrust is the force that opposes drag and moves a plane forward. Thrust is created by a plane's propeller or by its jet engines. When a plane's lift equals the force of gravity and its thrust equals the drag, the plane is level, cruising flight. When any of the four forces changes, the plane begins to climb , turn, or change its direction or position in some other way. I will like to discuss some of the ways in which the four basic forces affect the flight of an airplane. Let's take Gravity and Lift Gravity tends to keep an airplane on the ground or to pull it to the earth when in flight. The force of gravity on the ground equals the weight of the plane on the ground. For a plane to become airborne and to stay in the air, its wing must create a lifting force greater than the downward force of gravity. Lift is created by a change of air pressure around an airplane's wing as the plane moves along the ground or through the air. An airplane wing has a curved upper surface. As a plane moves forward, the pressure of the air that rushes over this curved surface falls. A high-pressure area always moves toward a low-pressure area. The high-pressure area below the wing thus rises toward the low-pressure area above it and so lifts the plane into the air. an airplane lifting  Isn't that beautiful? When a plane stands on the ground, the air pressure above and below its wing is the same. As the plane starts to move forward, air begins to flow over and under the wing. The air moving over the curved upper surface flows in a curve. As it does so, its speed increases and its pressure drops. The air moving under the flat bottom of the wing moves in a straight line. Its speed and pressure are not changed by the wing. A high-pressure area always moves toward a low-pressure area, and so the air under the wing tries to to move upward to the air over the wing.But the wing is in the way. Instead of meting the low-pressure area, the high-pressure area lifts the wing into the air. The faster the airplane moves, the greater the lift its wing produces. As an airplane increases its speed down the runway before take-off, its wing builds up more and more lift. The air pressure beneath the wing finally becomes greater than the weight of the plane, and so the force of the lift becomes greater than than the force of gravity.The plane then takes off. Lets talk about Drag and Thrust. Drag and Thrust A wing can produce lift only if it is moving forward through the air. A plane needs engine thrust to create the required forward movement. As thrust increases, it moves a plane forward faster than before. However, as a plane's speed increases, drag increases also. To oppose drag, the plane needs still more thrust. In a jet airplane, the rapid movement of gases through the jet engine produces thrust. Propellers produce thrust in turboprop and gasoline-powered planes. Propeller blaeds are shaped much like airplane wings. As the propeller spins, the air pressure on the front surface of the blades is reduced. The higher pressure on the back of the blades moves toward the lower pressure on the front. As it does so, it pushes against the propeller blades and moves the plane forward. The faster the jet engine works or the propeller spins, the greater the force of the thrust.To help increase thrust , engineers design airplane bodies to be as streamlined as possible. They give them a sleek, trim shape, and they design every part on the outside so that it will knife through the air easily and smoothly. Changing altitude An airplane cruising in level flight has lift balanced against gravity and thrust balanced against drag. To make the airplane descend, the pilot must decrease the power of the engine . The propeller or jet engines slow down, reducing the plane's thrust. The reduction in thrust also reduces lift, and the airplane begins to move downward. At the same time, drag increase its effect, which further slows the airplane and adds to the rate at which the plane descends. In order to climb, the pilot increases the engine power. The propeller or jet engines work faster, creating more thrust. The increased thrust also increases lift, and the plane begins to climb. However, climbing increases drag, and so the plane needs still more lift. To get the added lift, the Pilot increases the plane's angle of attack-that is, the angle at which the wing cuts through the air. The Pilot uses the controls to make the nose point up slightly so that the wing is at an upward angle to the path of the plane's flight. The flow of air over the upper part of the wing increases in speed , and the air pressure over the wing becomes less than the pressure over the wing in cruising flight. The area of high pressure under the wing moves toward the area of lower pressure over the wing , producing lift. But increasing the angle of attack disturbs the flow of air over the wing, which increases drag. The Pilot brings the four forces of flight into balance again by increasing engine power to gain more thrust. Changing direction A Pilot turns a plane by increasing the lift on one wing or the other. To make a left turn, for example, the Pilot operates controls that put the airplane into a left bank. That is, the left wing dips lower tahn the right one . Lift always occurs at a right angle to the surface of the wing. When the wing is not horizontal to the ground, lift takes place at an angle to the ground. As the wing dips, the lift on the right wing increases, which pulls the plane around the turn. The pilot uses the rudder is not used to turn the plane. It is the lifting force of the wing, occuring at an angle to the horizon, that makes the plane turn. When a plane makes a turn, the amount of lift opposing the force of gravity is reduced . As a result. the plane begins to lose altitude. To bring the four forces back into balance, the Pilot can do one ot two things. (1) The Pilot can increase the angle of attack and thus increase the lifting force of the wing. (2) The Pilot can increase the engine power to increase thrust. The increased thrust produces greater lift. In making a steep turn, a Pilot increases both the angle of attack and the engine power at the same time in order to keep the plane from losing altitude. This is where I end my discussion on aviation. If you have any comments or any other information or you want to contact me personally please click here: Ƴ
or send me a mail <[email protected]> |
||