-
Q01 |
- Diagram : Ellipse in Polar form
- Q02 | - Find ellipse in polar form
- Q03 | - Convert R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A)) to rectangular form
- Q04 | - Convert R = 1.8/(1 - 0.8*cos(A)) to rectangular form
- Q05 | - Reference
- Q02 | - Find ellipse in polar form
Q01. Diagram :
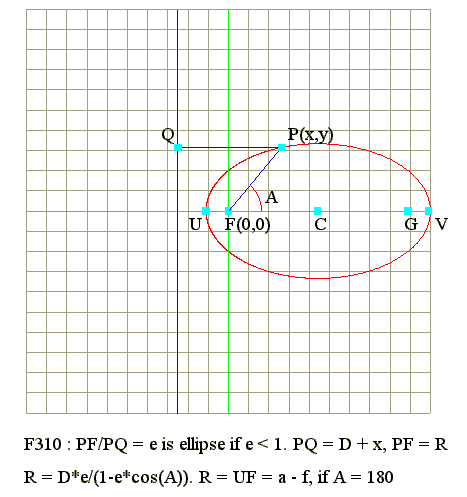
|
Go to Begin
Q02. Find ellipse in polar form
Solution
- Let origin be at F(0,0)
- Point P(x, y) on ellipse
- Point P to directrix is PQ = D + x
- PF = R and x = r*cos(A)
- Defintion : PF/PQ = e
- R/(D + x) = e
- R = e*(D + x) = e*(D + R*cos(A))
- Hence R*(1 - e*cos(A)) = D*e
- Hence R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A)) and e is less than 0
- 1. R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A)) : Origin at left focus
- 2. R = (D*e)/(1 + e*cos(A)) : Origin at right focus
- 3. R = (D*e)/(1 - e*sin(A)) : Origin at bottom focus
- 4. R = (D*e)/(1 + e*sin(A)) : Origin at top focus
- Compare diagrams of R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A)) with (x/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1
- When A = 180 degrees and cos(180) = -1
- R = FU = a - f
- R = (D*e)/(1 + e)
- Hence R = (D*e)/(1 + e) = a - f
- Hence D*e = (a - f)*(1 + e)
- Since e = f/a
- Hence D*e = (a^2 - f^2)/a
Go to Begin
Q03. Convert R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A)) to rectangular form
Solution : Use D
- The corresponding form
- Rectangular form : ((x - f)/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1
- Polar form : R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A))
- Since center at (0, 0) : (x/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1 ........... (1)
- Center at (f, 0) : ((x - f)/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1 ........... (2)
- Polar form center at (f, 0) : R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A)) .. (3)
- Since (1) and (2) give congruent diagram
- Hence we can translate center from (1) to (2)
- From (2) and (3), we see that (2) is the answer is the answer
- Also (1) is the answer
- R = D*e/(1 - e*cos(A))
- R*(1 - e*cos(A)) = D*e
- R - e*R*cos(A) = D*e
- R = D*e + e*x
- Since D*e = (b^2)/a and e = f/a
- Hence R = (b^2)/a + f*x/a
- Or a*R = b^2 + x*f
- Square both sides
- (a^2)*(R^2) = (b^2 + x*f)^2
- (a^2)*(R^2) = b^4 + 2*(b^2)*x*f + (x^2)*(f^2)
- (a^2)*(x^2 + y^2) - 2*(b^2)*x*f - (x^2)*(f^2) = b^4
- (a^2)*(x^2) + (a^2)*(y^2) - 2*(b^2)*x*f - (x^2)*(f^2) = b^4 .......... (1)
- Since b^2 = a^2 - f^2, (1) becomes
- (a^2 - f^2)*(x^2) + (a^2)*(y^2) - 2*(b^2)*x*f = (b^2)*(a^2 - f^2)
- (b^2)*(x^2 - 2*x*f + f^2) + (a^2)*(y^2) = (b^2)*(a^2) ............... (2)
- (b^2)*(x - f)^2 + (a^2)*(y^2) = (a^2)*(b^2)
- Divide both sides by (a^2)*(b^2)
- ((x - f)/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1
Go to Begin
Q04. Convert R = 1.8/(1 - 0.8*cos(A)) to rectangular form
Solution : Use D*e = (a^2 - f^2)/a = (b^2)/a and e = f/a
- The corresponding form
- ((x - f)/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1
- (x/a)^2 + (y/b)^2 = 1
- R = (D*e)/(1 - e*cos(A))
- For R = 1.8/(1 - 0.8*cos(A))
- e = 0.8
- D*e = 1.8 and D = 2.25
- e = f/a and f = 0.8*a ...... (1)
- D*e = (a^2 - f^2)/a
- 1.8*a = (a^2 - f^2) ........ (2)
- Substitute (1) into (2), we have
- 1.8*a = (a^2 - (0.8*a)^2)
- 1.8*a = 0.36*a^2
- a*(1.8 - 0.36*a) = 0
- Hence a = 0 or a = 1.8/0.36 = 5
- Substitute a = 5 into (1), Hence f = 4
- Since f^2 = a^2 - b^2
- Hence b^2 = a^2 - f^2 = 25 - 16 = 9
- Hence b = 3
- Hence equarion is (x/5)^2 + (y/3)^2 = 1
- General solution : ((x - h)/a)^2 + ((y - k)/b)^2 = 1
- R = 1.8/(1 - 0.8*cos(A))
- R*(1 - 0.8*cos(A)) = 1.8
- Since R^2 = x^2 + y^2 and x = R*cos(A)
- Hence R - 0.8*x = 1.8 or R = 1.8 + 0.8*x ......... (1)
- Square both sides of (1)
- x^2 + y^2 = 1.8^2 + 2*1.8*0.8*x + 0.64*x^2
- Simply 0.36*x^2 - 2.88*x + y^2 = 3.24 ............ (2)
- Use completing the square, (2) becomes
- 0.36*(x^2 - 8*x + 16 - 16) + y^2 = 3.24
- 0.36*(x - 4)^2 + y^2 = 3.24 + 0.36*16
- 0.36*(x - 4)^2 + y^2 = 9
- ((x - 4)/5)^2 + (y/3)^2 = 1
Go to Begin
Q05. Reference
Reference
Go to Begin
