|
Definitions of Diabetes on the Web: care of
Google
-
What is gestational diabetes?
Category: Mom's health A chronic health condition where the body is
unable to produce insulin and properly break down sugar (glucose) in the
blood. Symptoms include hunger, thirst, excessive urination, dehydration
and weight loss. The treatment of diabetes requires daily insulin
injections, proper nutrition and regular exercise.
- (dye-a-BEE-teez)
A disease in which the body does not
properly control the amount of sugar in the blood. As a result, the
level of sugar in the blood is too high. This disease occurs when the
body does not produce enough insulin or does not use it properly.
(MEL-ih-tus)
A group of disorders in which there
is a defect in the transfer of glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream
into cells, leading to abnormally high levels of blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
- A condition caused when the body is unable to use insulin to process
the glucose (sugar) in the blood properly and so the level of glucose in
the blood is too high for good health
- a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use
insulin, a hormone that is necessary to convert sugar, starches, and
other food into energy.
insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
- A lifelong disease marked by elevated levels of sugar in the blood.
It can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
a
- A disease in which the body's production and use of insulin is
impaired, causing sugar to build up in the bloodstream. There are many
types of diabetes, but the most common are type 1, type 2 and
gestational. Also called diabetes mellitus (MEL-lih-tuhs).
- a disease in which patients have high levels of sugar in their blood
- A disease in which blood glucose (blood sugar) levels are above
normal. Type 2 diabetes, also known as adult-onset or noninsulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), is the most common form of diabetes.
- an abnormal state of health marked by insulin is deficient and the
urine and blood contain excess sugar
- A disease in which the body cannot convert food into energy because
of a lack of insulin (a hormone produced by the pancreas), or because of
an inability to use insulin. Diabetes is a serious condition that can
cause complications ranging from numbness to loss of vision to coma. It
also significantly raises the risk for other problems, such as stroke
and heart disease. About 17 million Americans have diabetes.
- A disease associated with the absence or reduced levels of insulin,
a hormone produced by the pancreas that is essential for the transport
of glucose to cells.
- A disease that affects the metabolism of glucose (sugar), thus
causing changes in blood vessels. These changes may aid in the
development of coronary artery disease.
- a disease which causes a high glucose level and can cause kidney
failure - this develops in about 20% of all patients with diabetes.
- A hereditary or developmental problem with sugar metabolism. Caused
by a failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin. Juvenile
diabetes, or type 1 diabetes, is treated with diet, exercise and
insulin. Type 2, formerly called adult onset, is now seen in overweight
children. It is treated with diet, exercise and medication. In severe
cases, type 2 diabetes is also treated with insulin.
- A disease in which sugar and starch are not properly used by our
bodies due to inadequate insulin production (type 1) or decreased
sensitivity to insulin (type 2).
- An abnormality of insulin production that results in elevated blood
sugar. The elevated blood sugar can cause damage to many organs of the
body, including the retina.
- medical illness caused by too little insulin (insulin normally
lowers blood sugar) or poor response to insulin. As a result, blood
sugars are not well controlled and are higher than normal. It can affect
many parts of the body causing disease of small arteries, disease of
peripheral nerves, and can affect white blood cells ability to fight
infection.
- A condition that means your body cannot control the level of sugar
in the blood effectively. People with diabetes are very susceptible to
kidney failure because diabetes affects the blood supply to the kidneys.
There are two types of diabetes. Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetics
tend to develop the disease early in life and are unable to control
blood sugar levels because their bodies cannot make a special hormone
called insulin. ...
- mellitus. A common form of diabetes in which the body cannot
properly store or use glucose (sugar), the body's main source of energy.
- (dy-uh-BEE-teez): diabetes mellitus; a metabolic disease in which
deficient insulin leads to decreased carbohydrate utilization and
enhanced utilization of lipids and proteins
- a chronic condition associated with abnormally high levels of
glucose (sugar) in the blood. The two types of diabetes are referred to
as insulin-dependent (type I) and non-insulin dependent (type II). Type
I diabetes results from a lack of adequate insulin secretion by the
pancreas. Type II diabetes (also known as adult-onset diabetes) is
characterized by an insensitivity of the tissues of the body to insulin
secreted by the pancreas (insulin resistance).
- A chronic health condition in which the body is unable to break down
sugar and starches for energy. Complications can include heart disease,
stroke, neuropathy, poor circulation leading to loss of limbs, hearing
impairment, vision problems, and death. Type 1 (insulin-dependent)
diabetes, in which the body does not produce enough insulin, usually
appears in children and young adults. ...
- The inability of the body to produce or respond properly to insulin.
The body needs insulin to convert sugar and starch into the energy
needed in daily life. The full name for this condition is diabetes
mellitus; defined as a fasting blood glucose of 126 mg/dL or more
measured on two occasions.
- Diabetes mellitus is a medical disorder characterized by varying or
persistent hyperglycaemia (elevated blood sugar levels), especially
after eating. All types of diabetes mellitus share similar symptoms and
complications at advanced stages. Hyperglycaemia itself can lead to
dehydration and ketoacidosis. ...
Wikapedia - diabetes
|
I realise that is seems that Br Andrew
Efodoes all the writing for this web - true yet Jessica has firstly set
the work down. Jessica also produces and updates her Medical Protocols for
the benefit of her Respite Organisations and carers. The following table
is an example of one.
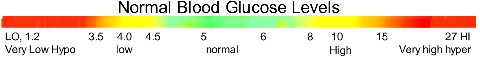
Jessica’s Blood glucose levels protocols
Hypoglycaemia is a low Blood Glucose Level of less than 4.0, at any
time.
You must start treatment immediately or
without immediate treatment, Jessica can go into a coma or die.
Symptoms of Hypoglycaemia:
May be mistaken for a Epileptic Seizure
|
Is Jessica behaving strangely or does
she appear drunk?
Jessica may have a loss of awareness
Jessica may have a change in awareness,
behaviour.
Jessica may also show abnormal activity
or behaviour.
Jessica’s blood sugar might be low
(less than 4.0). |
Answers, I’m ok, to all questions.
Pulls at her hair.
Pulls at her cloths.
Also giggles, when she is hurt or in
pain.
Giggles, even In a Seizure. |
If Jessica is conscious, & able to respond. Go to Step 1
Jessica is unconscious, or is unable to co-operate or
respond go straight to step 4
Step 1. Give
Jessica something sweet to eat e.g. 6 Jellybeans, Sugared Ginger, Dried
Fruit, 2 teaspoons/cubes of sugar or a sweetened drink.
Step 2. Re-test in
15 minutes,
If the B.G.L. is less than 4.5,
repeat steps 1 and 2, If the B.G.L. is over 4.5,
go to step 3.
Step 3.
Eating a Muffin, a Sandwich or biscuits
should keep the improvements continuing.
Blood glucose levels must return to between
4.5 & 8.0 Within 10 -15 minutes after Treatment.
If Jessica does not recover within 15
minutes, go straight to step 4
OR:
Jessica is
unconscious,
Jessica Is Unable to co-operate,
Jessica Will not,
co-operate, Jessica
Will not, respond,
Go straight to step 4
Step. 4
Call an ambulance immediately by
dialling 000 And Saying, “This is, a Diabetic Emergency
What to do and say, when you call an ambulance
1. Dial 000 (Police Fire or
ambulance) when answered ask for ambulance
2. when the ambulance
operator answers, Say, “This is, a Diabetic Emergency”
3. Say the address where you
are, any Land marks, and nearest cross Streets
(With Poor Mobile, reception areas only try
dialling 112)
Jessica must, follow the advice of the
ambulance officers at all times!
Signed
A J Blair.
|

